AUTHORITY: Implementing and authorized by Section 8 of the Illinois Groundwater Protection Act [415 ILCS 55/8] and authorized by Section 27 of the Illinois Environmental Protection Act [415 ILCS 5/27].
SOURCE: Adopted in R89-14(B) at 15 Ill. Reg. 17614, effective November 25, 1991; amended in R89-14(C) at 16 Ill. Reg. 14667, effective September 11, 1992; amended in R93-27 at 18 Ill. Reg. 14084, effective August 24, 1994; amended in R96-18 at 21 Ill. Reg. 6518, effective May 8, 1997; amended in R97-11 at 21 Ill. Reg. 7869, effective July 1, 1997; amended in R01-14 at 26 Ill. Reg. 2662, effective February 5, 2002; amended in R08-18 at 36 Ill. Reg. 15206, effective October 5, 2012; amended in R08-18(B) at 37 Ill. Reg. 16529, effective October 7, 2013; amended in R22-18 at 49 Ill. Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025.
Section 620.105 Purpose
This Part specifies requirements,
standards, and procedures for protecting and managing groundwater quality,
including groundwater classification, nondegradation, and groundwater quality
standards.
(Source:
Amended at 49 Ill. Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.110 Definitions
The definitions of the
Environmental Protection Act [415 ILCS 5] and the Groundwater Protection Act
[415 ILCS 55] apply to this Part. The following definitions also apply to this
Part;
"Act"
means the Environmental Protection Act [415 ILCS 5].
"Agency"
means the Illinois Environmental Protection Agency.
"Aquifer"
means saturated (with groundwater) soils and geologic materials that are
sufficiently permeable to readily yield economically useful quantities of water
to wells, springs, or streams under ordinary hydraulic gradients. [415 ILCS
55/3(b)]
"BETX"
means the sum of the concentrations of benzene, ethylbenzene, toluene, and
xylenes.
"Board"
means the Illinois Pollution Control Board.
"Carcinogen"
means a contaminant that is classified as a Category A1 or A2 Carcinogen by the
American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists; or a Category 1 or
2A/2B carcinogen by the World Health Organization's International Agency for
Research on Cancer; or a "Human carcinogen" or "Anticipated
Human Carcinogen" by the United States Department of Health and Human
Service National Toxicological Program; or a Category A or B1/B2 Carcinogen or
as "carcinogenic to humans" or "likely to become carcinogenic to
humans" by the United States Environmental Protection Agency in
Integrated Risk Information System or a Final Rule issued in a Federal Register
notice by the USEPA. [415 ILCS 5/58.2]
"Chemical
Abstracts Service Registry Number" or "CASRN" means a unique
numerical identifier designated for only one substance, assigned by the
Chemical Abstracts Service for the substance.
"Community
water supply" means a public supply that serves or is intended to
serve at least 15 service connections used by residents or regularly serves at
least 25 residents. [415 ILCS 5/3.145]
"Contaminant"
means any solid, liquid, or gaseous matter, any odor, or any form of energy,
from whatever source. [415 ILCS 5/3.165]
"Corrective
action process" means the procedures and practices that a regulatory
agency may perform, require, or otherwise oversee, including corrective action
and controls and management, to address a potential or existing violation of any
Subpart D standard due to a release of one or more contaminants.
BOARD NOTE:
This definition includes the performance of activities that, under Section
620.450(a)(3), stay the applicability of otherwise applicable standards
specified in Section 620.410, 620.420, 620.430, or 620.440. This definition
also includes the implementation of controls and management, under Section
620.250(d)(2) and (e), after the completion of corrective action.
"Cumulative
impact area" means the area, including the coal mine area permitted under
the Surface Coal Mining Land Conservation and Reclamation Act [225 ILCS 720]
and 62 Ill. Adm. Code 1700 through 1850, within which impacts resulting from
the proposed operation may interact with the impacts of all anticipated mining
on surface water and groundwater systems.
"Detection"
means the identification of a contaminant in a sample at a value equal to or
greater than the:
"Method detection
limit" or "MDL"; or
"Lower limit
of quantitation" or "LLOQ".
"Groundwater"
means underground water that occurs within the saturated zone and
geologic materials where the fluid pressure in the pore space is equal to or
greater than atmospheric pressure. [415 ILCS 5/3.210]
"Hydrologic
balance" means the relationship between the quality and quantity of water
inflow to, water outflow from, and water storage in a hydrologic unit, such as
a drainage basin, aquifer, soil zone, lake, or reservoir. It encompasses the
dynamic relationships among precipitation, runoff, evaporation, and changes in
ground and surface water storage.
"IGPA"
means the Illinois Groundwater Protection Act. [415 ILCS 55]
"Lower limit
of quantitation" or "LLOQ" means the minimum concentration of a
substance that can be measured or reported under "Test Methods of
Evaluation Solid Wastes, Physical/Chemical Methods", incorporated by
reference in Section 620.125.
"Lowest concentration minimum
reporting level" or "LCMRL" means the lowest spiking
concentration such that the probability of spike recovery in the 50% or 150%
range is at least 99%.
"Lowest
observable adverse effect level" or "LOAEL" means the lowest
tested concentration of a chemical or substance that produces a statistically
significant increase in frequency or severity of non-overt adverse effects
between the exposed population and its appropriate control.
"Licensed
Professional Engineer" or "LPE" means a person,
corporation, or partnership licensed under the laws of the State of Illinois to
practice professional engineering. [415 ILCS 5/57.2]
"Licensed
Professional Geologist" or "LPG" means an individual who
is licensed under the Professional Geologist Licensing Act to engage in
the practice of professional geology in Illinois. [225 ILCS 745/15]
"Method detection limit"
or "MDL" means the minimum measured concentration of a substance that
can be reported with 99% confidence that the measured concentration is
distinguishable from method blank results as determined under 40 CFR 136,
appendix B (2017), incorporated by reference in Section 620.125.
"Mutagen"
means a carcinogen that can induce an alteration in the structure of DNA.
"No
observable adverse effect level" or "NOAEL" means the highest
tested concentration of a chemical or substance that does not produce a
statistically significant increase in frequency or severity of non-overt
adverse effects between the exposed population and its appropriate control.
"Non-community
water supply" means a public water supply that is not a community water
supply. [415 ILCS 5/3.145]
"Off-site"
means not on-site.
"On-site"
means on the same or geographically contiguous property that may be divided by
public or private right-of-way, if the entrance and exit between properties is
at a crossroads intersection and access is by crossing as opposed to going
along the right-of-way. Noncontiguous properties owned by the same person but
connected by a right-of-way that he or she controls and that the public does
not have access to is also considered on-site property.
"Operator"
means the person responsible for the operation of a site, facility, or unit.
"Owner"
means the person who owns a site, facility, or unit, or part of a site,
facility, or unit, or who owns the land on which the site, facility, or unit is
located.
"Potable"
means generally fit for human consumption in compliance with accepted
water supply principles and practices. [415 ILCS 5/3.340]
"Potential
primary source" means any unit at a facility or site not currently subject
to a removal or remedial action that:
Is used
for the treatment, storage, or disposal of any hazardous or special waste not
generated at the site; or
Is used
for the disposal of municipal waste not generated at the site, other than
landscape waste and construction and demolition debris; or
Is used
for the landfilling, land treating, surface impounding, or piling of any
hazardous or special waste that is generated on the site or at other sites
owned, controlled, or operated by the same person; or
Stores or
accumulates at any time more than 75,000 pounds above ground, or more than
7,500 pounds below ground, of any hazardous substances. [415 ILCS 5/3.345]
"Potential
route" means abandoned and improperly plugged wells of all kinds, drainage
wells, all injection wells, including closed loop heat pump wells, and any
excavation for the discovery, development or production of stone, sand, or
gravel. This term does not include closed loop heat pump wells using USP
(U.S. Pharmacopeia) food grade propylene glycol. [415 ILCS 5/3.350]
"Potential
secondary source" means any unit at a facility or a site not currently
subject to a removal or remedial action, other than a potential primary source,
that:
Is used
for the landfilling, land treating, or surface impounding of waste that is
generated on the site or at other sites owned, controlled, or operated by the
same person, other than livestock and landscape waste, and construction and
demolition debris; or
Stores or
accumulates at any time more than 25,000 but not more than 75,000 pounds above
ground, or more than 2,500 but not more than 7,500 pounds below ground, of any
hazardous substance; or
Stores or
accumulates at any time more than 25,000 gallons above ground, or more than 500
gallons below ground, of petroleum, including crude oil or any fraction of
crude oil that is not otherwise specifically listed or designated as a
hazardous substance; or
Stores or
accumulates pesticides, fertilizers, or road oils for commercial application or
for distribution to retail sales outlets; or
Stores or
accumulates at any time more than 50,000 pounds of any de-icing agent; or
Is used
for handling livestock waste or for treating domestic wastewaters other than
private sewage disposal systems as defined in the Private Sewage Disposal
Licensing Act [225 ILCS 225]. [415 ILCS 5/3.355]
"Previously
mined area" means land disturbed or affected by coal mining operations before
February 1, 1983.
BOARD NOTE:
February 1, 1983, is the effective date of the Illinois Department of Natural
Resources Permanent Program regulations (62 Ill. Adm. Code 1800 through 1850) implementing
the Surface Coal Mining Land Conservation and Reclamation Act [225 ILCS 720],
as specified in 62 Ill. Adm. Code 1700.11(c).
"Property
class" means the class assigned by a tax assessor to real property for
real estate taxes.
BOARD NOTE:
The property class (rural property, residential vacant land, residential with
dwelling, commercial residence, commercial business, commercial office, or
industrial) is identified on the property record card maintained by the tax
assessor in compliance with the Illinois Real Property Appraisal Manual
(February 1987), published by the Illinois Department of Revenue, Property Tax
Administration Bureau.
"Public
water supply" means all mains, pipes, and structures through which water
is obtained and distributed to the public, including wells and well structures,
intakes and cribs, pumping stations, treatment plants, reservoirs, and storage
tanks and appurtenances, collectively or severally, actually used or intended
for use for furnishing water for drinking or general domestic use, and that
serve at least 15 service connections or that regularly serve at least
25 persons at least 60 days per year. A public water supply is either a
"community water supply" or a "non-community water supply".
[415 ILCS 5/3.365]
"Regulated
entity" means a facility or unit regulated for groundwater protection by
any State or federal agency.
"Regulated
recharge area" means a compact geographic area, as determined by the Board
under Section 17.4 of the Act, the geology of which renders a potable
resource groundwater particularly susceptible to contamination. [415 ILCS
5/3.390]
"Regulatory
agency" means the Illinois Environmental Protection Agency, Department of
Public Health, Department of Agriculture, the Office of Mines and Minerals and
the Office of Oil and Gas Resource Management in the Department of Natural
Resources, and the Office of State Fire Marshal.
"Resource
groundwater" means groundwater that is presently being, or in the future
is capable of being, put to beneficial use by reason of being of suitable
quality. [415 ILCS 5/3.430]
"Saturated
zone" means a subsurface zone in which all the interstices or voids are
filled with water under pressure greater than that of the atmosphere.
"Setback
zone" means a geographic area, designated under the Act, containing
a potable water supply well or a potential source or potential route having a
continuous boundary, and within which specified prohibitions or
regulations apply to protect groundwaters. [415 ILCS 5/3.450]
"Site"
means any location, place, tract of land, and facilities, including buildings
and improvements used for purposes subject to regulation or control by the Act
or regulations under the Act. [415 ILCS 5/3.460]
"Spring"
means a natural surface discharge of an aquifer from rock or soil.
"Threshold
dose" means the lowest dose of a chemical at which a specified measurable
effect is observed and below which it is not observed.
"Treatment"
means the technology, treatment techniques, or other procedures for compliance
with 35 Ill. Adm. Code, Subtitle F.
"Unit"
means any device, mechanism, equipment, or area (exclusive of land used
only for agricultural production). This term includes secondary
containment structures and their contents at agrichemical facilities. [415
ILCS 5/3.515]
"USEPA"
means the United States Environmental Protection Agency.
"Wellhead protection area"
or "WHPA" means the surface and subsurface recharge area surrounding
a community water supply well or well field, delineated outside of any
applicable setback zones under Section 17.1 of the Act [415 ILCS 5/17.1] and
Illinois' Wellhead Protection Program, through which contaminants are
reasonably likely to move toward that well or well field.
"Wellhead Protection Program"
or "WHPP" means the wellhead protection program for the State of
Illinois, approved by USEPA under 42 U.S.C. 300h-7.
BOARD NOTE: Derived from 40 CFR
141.71(b) (2003). The wellhead protection program includes the "groundwater
protection needs assessment" under Section 17.1 of the Act [415 ILCS
5/17.1] and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 615-617.
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill.
Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.115 Prohibition
A person must not cause,
threaten, or allow a violation of the Act, the IGPA, or regulations adopted by
the Board under either statute, including this Part.
(Source:
Amended at 49 Ill. Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.125
Incorporations by Reference
a) The Board incorporates the following material by reference:
ASTM
International. 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959
(610) 832-9500.
"Standard
Practice for Classification of Soils for Engineering Purposes (Unified
Classification System)" ASTM D2487-06.
"Standard
Test Method for Determination of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Water,
Sludge, Influent, Effluent, and Wastewater by Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass
Spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) ASTM D7979-20.
CFR (Code of Federal
Regulations). Available from the Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government
Printing Office, Washington, D.C. 20402 (202) 783-3238.
Method Detection Limit Definition,
appendix B to Part 136, 40 CFR 136, appendix B − Revision 2 (82 FR 40939,
Aug. 28, 2017).
Control of Lead and Copper,
general requirements, 40 CFR 141.80 (72 FR 57814, Oct. 10, 2007).
Maximum contaminant levels for
organic contaminants, 40 CFR 141.61 (59 FR 34324, July 1, 1994).
Maximum contaminant levels for
inorganic contaminants, 40 CFR 141.62 (69 FR 38855, June 29, 2004).
Maximum contaminant levels for
radionuclides, 40 CFR 141.66 (65 FR 76748, Dec. 7, 2000).
GPO.
Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C. 20401
(202) 783-3238.
USEPA
Guidelines for Carcinogenic Risk Assessment, 51 Fed. Reg. 33992-34003
(September 24, 1986).
Illinois Environmental Protection
Agency, 2520 W. Iles Ave., P.O. Box 19276, Springfield, IL 62794-9276 (217)
785-4787.
"Guidance Document for
Groundwater Protection Needs Assessments", Agency, Illinois State Water
Survey, and Illinois State Geologic Survey Joint Report, January 1995.
"Illinois Integrated Water
Quality Report and Section 303(d) List, 2020/2022", Agency, June 2022.
"The Illinois Wellhead
Protection Program Pursuant to Section 1428 of the Federal Safe Drinking Water
Act", Agency, # 22480, October 1992.
Illinois Pollution Control Board,
60 E. Van Buren, Suite 630, Chicago, IL 60605 (312) 814-3669.
"Class III Groundwater
Listing Notice Fogelpole Cave Nature Preserve", Environmental Register, No.
587, May 2003.
"Class III Groundwater
Listing Notice Pautler Cave Nature Preserve and Stemler Cave Nature
Preserve", Environmental Register, No. 611, May 2005.
"Class III Groundwater
Listing Notice Armin Kruger Speleological Area", Environmental Register, No.
666, Dec. 2009.
"Class III Groundwater
Listing Notice Cotton Creek Marsh Nature Preserve and Spring Grove Fen Nature
Preserve", Environmental Register, No. 697, July 2012.
BOARD NOTE: The Environmental
Register is a Board publication available on the Board's website at https://pcb.illinois.gov/Resources/EnvironmentalRegister.
NAS National
Academy of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine,
500 5th
St. NW, Washington DC, 20001 (202) 334-2000.
"Water
Quality Criteria 1972", EPA.R3.73-033, 1973. https://nepis.epa.gov
NCRP. National
Council on Radiation Protection, 7910 Woodmont Ave., Bethesda, MD (301)
657-2652.
"Maximum
Permissible Body Burdens and Maximum Permissible Concentrations of
Radionuclides in Air and in Water for Occupational Exposure", NCRP Report
Number 22, June 5, 1959.
USEPA, 1200
Pennsylvania Avenue, N. W., Washington DC, 20460 (202) 564-4700.
"Low
Stress (low flow) Purging and Sampling Procedure for the Collection of
Groundwater Samples from Monitoring Wells", EPA Publication EQASOP-GW4,
Region 1 Low-Stress (low flow) SOP Revision No. 4, July 30, 1996; revised
September 19, 2017.
"Methods for Chemical
Analysis of Water and Wastes", March 1983, Doc. No. PB84-128677. EPA
600/4-79-020 (available online at http://nepis.epa.gov/).
"Methods for the
Determination of Inorganic Substances in Environmental Samples", August
1993, PB94-120821 (referred to as "USEPA Environmental Inorganic Methods").
EPA 600/R-93-100 (available online at http://nepis.epa.gov/).
"Methods for the
Determination of Metals in Environmental Samples", June 1991, Doc. No.
PB91-231498. EPA 600/4-91-010 (available online at http://nepis.epa.gov/).
"Methods for the
Determination of Metals in Environmental Samples − Supplement I",
May 1994, Doc. No. PB95-125472. EPA 600/R-94-111 (available online at
http://nepis.epa.gov/).
"Methods for the
Determination of Organic Compounds in Drinking Water", Doc. No.
PB91-231480. EPA/600/4-88/039 (December 1988 (revised July 1991)) (available
online at http://nepis.epa.gov/).
"Methods for the
Determination of Organic Compounds in Drinking Water, Supplement I", Doc.
No. PB91-146027. EPA/600/4-90/020 (July 1990) (available online at
http://nepis.epa.gov/).
"Methods for the
Determination of Organic Compounds in Drinking Water, Supplement II", Doc.
No. PB92-207703. EPA/600/R-92/129 (August 1992) (available online at
http://nepis.epa.gov/).
"Methods for the
Determination of Organic Compounds in Drinking Water, Supplement III",
Doc. No. PB95-261616. EPA/600/R-95/131 (August 1995) (available online at
http://nepis.epa.gov/).
"Methods for the
Determination of Organic and Inorganic Compounds in Drinking Water" Volume
I: EPA 815-R-00-014 (August 2000) (available online at http://nepis.epa.gov/).
"Prescribed Procedures for
Measurement of Radioactivity in Drinking Water", Doc. No. PB80-224744.
EPA 600/4-80-032, (August 1980) (available online at http://nepis.epa.gov/).
"Procedures for Radiochemical
Analysis of Nuclear Reactor Aqueous Solutions", H.L. Krieger and S. Gold,
Doc. No. PB222-154/7BA. EPA-R4-73-014, May 1973.
"Radiochemical Analytical
Procedures for Analysis of Environmental Samples", March 1979, Doc. No.
EMSL LV 053917.
"Radiochemistry Procedures
Manual", Doc. No. PB-84-215581. EPA-520/5-84-006, December 1987.
"Selected Analytical Methods
for Environmental Remediation and Recovery (SAM) 2017". Record last revision
date February 10, 2020.
https://cfpub.epa.gov/si/si_public_record_report.cfm?Lab=NHSRC&dirEntryId=339252.
"Test
Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste, Physical/Chemical Methods", USEPA
Publication No. SW-846, Third Edition, Final Updates I (1993), II (1995), IIA
(1994), IIB (1995), III (1997), IIIA (1999), IIIB (2005), IV (2008), V (2015),
VI Phase 1 (2017), VI Phase 2 (2018), VI Phase 3 (2019), and VII Phase 1
(2020). http://www.epa.gov/hw-sw846/sw-846-compendium.
USEPA, Office of Ground Water and Drinking
Water, Standards and Risk Management Division.
"Method 533: Determination
of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Drinking Water by Isotope Dilution
Anion Exchange Solid Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry",
November 2019.
https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2019-12/documents/method-533-815b19020.pdf.
USEPA, Office of Research and
Development, Center for Environmental Solutions & Emergency Response
Shoemaker, J. and Dan Tettenhorst,
Method 537.1: Determination of selected Per- and Polyfluorinated Alkyl
Substances in Drinking Water by Solid Phase Extraction and Liquid
Chromatography/Tandem Mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS). U.S. Environmental
Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, Center for Environmental
Assessment, Washington, DC. Version 2.0, March 2020.
USEPA, Office of Resource
Conservation and Recovery.
"Statistical Analysis of
Groundwater Monitoring Data at RCRA Facilities, (March 2009 Unified
Guidance)", EPA 530/R-09-007.
USEPA, Office of Water,
Engineering and Analysis Division
USEPA, Office of Water,
Engineering and Analysis Division. "Method 1633: Analysis of Per- and
Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Aqueous, Solid, Biosolids, and Tissue
Samples by LC-MS/MS," January 2024, EPA 821-R-24-001.
USEPA, Risk Assessment forum,
Washington, D.C.
"A Review of the Reference
Dose and References Concentration Process", EPA/630/P-02/002F, December
2002.
"Guidance for Applying
Quantitative Data to Develop Data-Derived Extrapolation Factors for
Interspecies and Intraspecies Extrapolation", EPA/R-14/002F, September
2014.
"Guidelines for Carcinogen
Risk Assessment", EPA/630/P-03/001F, March 2005.
"Supplemental
Guidance for Assessing Susceptibility for Early-Life Exposure to
Carcinogens", EPA/630/R-03/003F, March 2005.
United States
Geological Survey, 1961 Stout St., Denver, CO 80294 (303) 844-4169
"Techniques
of Water Resources Investigations of the United States Geological Survey,
Guidelines for Collection and Field Analysis of Ground-Water Samples for
Selected Unstable Constituents", Book I, Chapter D2 (1976).
b) This Section incorporates no later editions or amendments.
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill.
Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.130 Exemption
from General Use Standards and Public and Food Processing Water Supply
Standards
Groundwater is not required to
meet the general use standards and public and food processing water supply
standards of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 302.Subparts B and C.
Section 620.135 Exclusion
for Underground Water in Certain Man-Made Conduits
This Part does not apply to
underground waters contained in man-made subsurface drains, tunnels,
reservoirs, storm sewers, tiles or sewers.
Section 620.201 Groundwater
Designations
All groundwaters of the State
are designated as:
a) One of the following four classes of groundwater under
Sections 620.210 through 620.240:
1) Class I: Potable Resource Groundwater;
2) Class II: General Resource Groundwater;
3) Class III: Special Resource Groundwater; or
4) Class IV: Other Groundwater;
b) A groundwater management zone established under Section
620.250; or
c) A groundwater management zone established under 35 Ill. Adm.
Code 740.530. See Section 620.250(h)-(j).
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill. Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.210 Class I: Potable
Resource Groundwater
Except as provided in Section
620.230, 620.240, or 620.250, Potable Resource Groundwater is as described in
subsection (a) or (b):
a) Groundwater that is 10 feet or more below the land surface and
within:
1) The minimum setback zone of a well that serves as a potable
water supply and to the bottom of the well;
2) Unconsolidated sand, gravel, or sand and gravel that is 5 feet
or more in thickness and contains 12% or less of fines (i.e., fines that pass
through a No. 200 sieve tested in compliance with ASTM Standard Practice D2487-06,
incorporated by reference in Section 620.125);
3) Sandstone that is 10 feet or more in thickness or fractured
carbonate that is 15 feet or more in thickness;
4) Any geologic material that is capable of a:
A) Sustained groundwater yield, from up to a 12-inch borehole, of at
least 150 gallons per day from a thickness of 15 feet or less; or
B) Hydraulic conductivity of 1 x 10-4 cm/sec or greater
using one of the following test methods or its equivalent:
i) Slug test; or
ii) Pump test;
5) A wellhead
protection area, as defined in Section 620.110, that is a Phase I or Phase II
wellhead protection area delineated in compliance with the "Guidance
Document for Groundwater Protection Needs Assessments" and "The
Illinois Wellhead Protection Program", both incorporated by reference in
Section 620.125; or
6) The
maximum setback zone of a community water supply well adopted under Section
14.3 of the Act.
b) Groundwater that is determined by the Board, under the
procedures specified in Section 620.260, to be capable of potable use.
BOARD NOTE:
In determining whether geologic material meets a subsection (a)(2) or (a)(3)
thickness minimum or the subsection (a)(4)(A) thickness maximum, the entire
thickness of the geologic material is considered, regardless of whether all or
only some of the thickness is 10 feet or more below the land surface. For example,
groundwater that is 10 feet or more below the land surface and within any
geologic material described in subsection (a)(2), (a)(3), or (a)(4)(A) is
designated as Class I: Potable Resource Groundwater, even if some of the
geologic material's thickness is within 10 feet of the land surface. In
addition, if groundwater that is 10 feet or more below the land surface – and
within any region or geologic material described in subsection (a) – also
extends upward to within 10 feet of the land surface, then the groundwater 10
feet or more below the land surface is designated as Class I: Potable Resource
Groundwater but the groundwater within 10 feet of the land surface is not.
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill.
Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.220 Class II: General
Resource Groundwater
Except as provided in Section
620.250, General Resource Groundwater is as described in subsection (a) or (b):
a) Groundwater that does not meet Section 620.210 (Class I),
Section 620.230 (Class III), or Section 620.240 (Class IV); or
b) Groundwater that is determined by the Board, under the
procedures specified in Section 620.260, to be capable of agricultural,
industrial, recreational, or other beneficial uses.
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill. Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.230 Class III: Special
Resource Groundwater
Except as provided in Section
620.250, Special Resource Groundwater is as described in subsection (a) or (b):
a) Groundwater that is determined by the Board, under the
procedures specified in Section 620.260, to be:
1) Demonstrably unique (e.g., irreplaceable sources of
groundwater) and suitable for application of a groundwater quality standard
more stringent than the otherwise applicable groundwater quality standard
specified in Subpart D; or
2) Vital for a particularly sensitive ecological system.
b) Groundwater that contributes to a dedicated nature preserve
that is listed by the Agency as specified below:
1) A written request to list a dedicated nature preserve under
this subsection must contain the following information:
A) A general description of the site and the surrounding land use;
B) A topographic map or other map of suitable scale denoting the location
of the dedicated nature preserve;
C) A general description of the existing groundwater quality at
and surrounding the dedicated nature preserve;
D) A general geologic profile of the dedicated nature preserve
based upon the most reasonably available information, including geologic maps
and subsurface groundwater flow directions; and
E) A description of the interrelationship between groundwater and
the nature of the site.
2) Upon confirmation by the Agency of the technical adequacy of a
written request, the Agency must publish the proposed listing of the dedicated
nature preserve in the Environmental Register for a 45-day public comment
period. Within 60 days after the close of the public comment period, the Agency
must either publish a final listing of the dedicated nature preserve in the
Environmental Register or provide a written response to the requestor
specifying the reasons for not listing the dedicated nature preserve.
3) At least once annually, the Agency must publish in the
Environmental Register a complete listing of all dedicated nature preserves
listed under this subsection.
4) For this subsection "dedicated nature preserve"
means a nature preserve that is dedicated under the Illinois Natural Areas
Preservation Act [525 ILCS 30].
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill. Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.240 Class IV:
Other Groundwater
Except as provided in Section
620.250, Other Groundwater is as described in subsection (a), (b), (c), (d),
(e), (f), (g), or (h).
a) Groundwater within a zone of attenuation under 35 Ill. Adm.
Code 811 and 814.
b) Groundwater within a point of compliance under 35 Ill. Adm.
Code 724, but not to exceed a lateral distance of 200 feet from the edge of a
potential primary or secondary source.
c) Groundwater that naturally contains more than 10,000 mg/L of
total dissolved solids.
d) Groundwater that has been designated by the Board as an exempt
aquifer under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 730.104.
e) Groundwater that underlies a potential primary or secondary
source, in which contaminants may be present from a release, if the owner or
operator of the source notifies the Agency in writing and the following
conditions are met:
1) The outermost edge of what would be considered the Class IV
groundwater is the closest practicable distance from the source, but does not
exceed:
A) A lateral distance of 25 feet from the edge of the potential
source or the property boundary, whichever is less, and
B) A depth of 15 feet from the bottom of the potential source or
the land surface, whichever is greater;
2) The source of any release of contaminants to groundwater has
been controlled;
3) Migration of contaminants within the site resulting from a
release to groundwater has been minimized;
4) Any on-site release of contaminants to groundwater has been
managed to prevent migration off-site; and
5) No potable water well exists within the outermost edge as specified
in subsection (e)(1).
f) Groundwater that underlies a coal mine refuse disposal area
not contained within an area from which overburden has been removed, a coal
combustion waste disposal area at a surface coal mine authorized under Section
21(s) of the Act, or an impoundment that contains sludge, slurry, or
precipitated process material at a coal preparation plant, in which
contaminants may be present, if the area or impoundment began operating after
February 1, 1983, the owner and operator notifies the Agency in writing, and
the following conditions are met:
1) The outermost edge of what would be considered the Class IV
groundwater is the closest practicable distance from the area or impoundment,
but does not exceed:
A) A lateral distance of 25 feet from the edge of the area or
impoundment, or the property boundary, whichever is less; and
B) A depth of 15 feet from the bottom of the area or impoundment,
or the land surface, whichever is greater;
2) The source of any release of contaminants to groundwater has
been controlled;
3) Migration of contaminants within the site resulting from a
release to groundwater has been minimized;
4) Any on-site release of contaminants to groundwater has been
managed to prevent migration off-site; and
5) No potable water well exists within the outermost edge as specified
in subsection (f)(1).
g) Groundwater within a previously mined area, unless monitoring
demonstrates that the groundwater is capable of consistently meeting the
standards of specified in Section 620.410 or 620.420. If that capability is
determined, groundwater within the previously mined area must not be considered
Class IV.
h) Groundwater regulated under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 845.
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill. Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.250 Groundwater
Management Zone
a) Within any class of groundwater, a groundwater management zone
(GMZ) may be established as a three-dimensional region containing groundwater
being managed to mitigate impairment caused by the release of one or more contaminants
that is subject to a corrective action process approved by the Agency.
b) Before
a GMZ may be established, the owner or operator of a site at which there has
been a release of one or more contaminants to groundwater must submit to the
Agency a GMZ application. The application must contain the information required
by Section 620.Appendix D, Parts I, II, and III, as well as any other information
requested in writing by the Agency that is relevant to its review under
subsection (c).
1) If
the GMZ would extend off-site, the GMZ application must include each off-site property
owner's written permission to the establishment of the GMZ on its property. If
effectively implementing the off-site portion of the GMZ requires accessing an
off-site property, the GMZ application must also include the off-site property
owner's written permission for that access. If the applicable written
permission or permissions from an off-site property owner are not obtained –
whether permission to establish the GMZ off-site, access the off-site property,
or both – the GMZ will not include that off-site property.
2) Nothing
in this subsection (b) precludes the owner or operator from including
additional information in its GMZ application.
3) Nothing
in this subsection (b) requires that a GMZ application be in the form specified
in Section 620.Appendix D, Parts I, II, and III.
c) The
Agency must review each GMZ application submitted under subsection (b) and
issue a written determination approving or rejecting the GMZ.
1) In
determining whether to approve a GMZ, the Agency must consider the substantive
information provided in support of the GMZ, the technical sufficiency of the
GMZ, the likelihood that the GMZ will protect public health and the
environment, and the likelihood that the GMZ's corrective action process will,
in a timely manner, result in compliance with the applicable standards specified
in Section 620.410, 620.420, 620.430, or 620.440 or otherwise minimize
exceedances to restore beneficial use as appropriate for the class or classes
of groundwater. If the Agency rejects a GMZ, the Agency must, in its written
determination, specify the reasons for the rejection.
2) A GMZ is established when the Agency issues a written
determination approving the GMZ, including its corrective action process. Once
a GMZ is established and before the corrective action is complete, the Agency
may, as new information warrants and subject to the standards of subsection
(c)(1), issue written determinations amending any part of the GMZ, including
its size, the contaminants that are subject to it, and its corrective action
process, as provided in this subsection (c)(2). A GMZ is amended when the
Agency issues a written determination amending the GMZ. If the Agency rejects
a submittal of the site owner or operator to amend the GMZ under subsection
(c)(2)(i) or (c)(2)(ii), the Agency must do so in a written determination that
specifies the reasons for the rejection.
i) The Agency may issue a written determination directing that
the site owner or operator submit to the Agency a written proposal to amend the
GMZ, consistent with subsection (b). The Agency's determination must identify
the amendment to be proposed and specify the reasons why the amendment is
necessary. If the owner or operator fails to submit a proposal or the Agency
rejects the proposal, the Agency may terminate the GMZ under subsection (f)
either on its own initiative or at the written request of the owner or
operator.
ii) If it wishes to have the Agency amend the GMZ, the site owner
or operator must submit to the Agency a written proposal to amend the GMZ,
consistent with subsection (b). If the Agency rejects the proposal, the Agency
may terminate the GMZ under subsection (f) either on its own initiative or at
the written request of the owner or operator.
d) When it completes the corrective action under subsection
(c)(2), the site owner or operator must submit to the Agency a written demonstration
that complies with subsection (d)(1) or (d)(2) and contains the information
required by the completion certification specified in Section 620.Appendix D,
Part IV. The Agency must review this demonstration and issue a written
determination approving or rejecting the demonstration. Nothing in this
subsection (d) requires the owner or operator to make the demonstration using any
specific type of documentation or precludes the owner or operator from
including additional information in the demonstration.
1) The
owner or operator must demonstrate that it has completed the corrective action
under subsection (c)(2) and the applicable standards of Subpart D, as specified
in Section 620.450(a)(4)(A), have been attained in groundwater within the GMZ.
If the Agency approves this demonstration, the Agency must issue a written
determination to that effect in which the Agency terminates the GMZ. The
termination takes effect when the Agency issues this determination. If the
Agency rejects this demonstration, the Agency must, in its written
determination, specify the reasons for the rejection, which may include the
Agency's basis for amending the GMZ to require additional corrective action
under subsection (c)(2).
2) The
owner or operator must demonstrate that it has completed the corrective action
under subsection (c)(2) and concentrations of released chemical constituents,
as specified in Section 620.450(a)(4)(B), remain in groundwater within the
GMZ. The owner or operator must also demonstrate compliance with Section
620.450(a)(4)(B)(i) and (ii), as well as the on-going adequacy of controls,
management, or both, as applicable, to maintain compliance with Section
620.450(a)(4)(B)(i) and (ii). If the Agency approves this demonstration, the
Agency must issue a written determination to that effect in which the Agency
states that the GMZ remains in effect. If the Agency rejects this demonstration,
the Agency must, in its written determination, specify the reasons for the
rejection, which may include the Agency's basis for amending the GMZ to require
additional corrective action under subsection (c)(2).
e) Within
five years after the Agency issues a written determination approving a
demonstration under subsection (d)(2), the site owner or operator must submit a
report to the Agency demonstrating the on-going adequacy of controls,
management, or both, as applicable, to maintain compliance with Section
620.450(a)(4)(B)(i) and (ii). The Agency must review the report and issue a
written determination approving or rejecting the demonstration.
1) The
submittal of these reports by the owner or operator and the corresponding
issuance of these written determinations by the Agency must occur at least
every five years while the GMZ remains in effect. If the Agency rejects a
demonstration, the Agency must, in its written determination, specify the
reasons for the rejection, which may include the Agency's basis for amending
the GMZ to require additional controls or management under this subsection (e).
2) Any
amendment to controls or management under this subsection (e) is subject to the
amendment provisions of subsection (c)(2), except that the standard for the
Agency’s determination is whether the controls or management, as amended, would
be adequate to maintain compliance with Section 620.450(a)(4)(B)(i) and (ii)
f) Without
limiting any other legal authority of the Agency to terminate a GMZ, the Agency
may issue a written determination terminating a GMZ based on any of the grounds
specified in this subsection (f). The determination must specify the grounds
for terminating the GMZ. The termination takes effect when the Agency issues
this determination. The Agency may terminate a GMZ if:
1) The site
owner or operator fails to perform or comply with the schedule for any part of
the GMZ, including its corrective action under subsection (c)(2) or its controls
or management under subsection (d)(2) or (e);
2) The
Agency rejects a proposal to amend the GMZ under subsection (c)(2) or a
demonstration under subsection (d) or (e);
3) The site
owner or operator commits fraud or misrepresentation in any submittal under
subsection (b), (c)(2), (d), or (e);
4) The
site owner or operator submits to the Agency a written request to terminate the
GMZ under subsection (c)(2); or
5) The
Agency, after issuing a written determination approving a demonstration under
subsection (d)(2), determines that
i) The
applicable standards specified in Section 620.410, 620.420, 620.430, or 620.440
have been attained in groundwater within the GMZ; or
ii) Additional
corrective action is necessary because controls and management are no longer
adequate to maintain compliance with Section 620.450(a)(4)(B)(i) and (ii).
g) Upon
GMZ termination under subsection (f), the groundwater within the
three-dimensional region formerly encompassed by the GMZ becomes both
designated as one of the four classes of groundwater specified in Section
620.201(a) and subject to the standards for the applicable class of groundwater
specified in Section 620.410, 620.420, 620.430, or 620.440.
h) Regardless of subsections (a) through (c), a "groundwater
management zone", as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 740.120, may be
established under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 740.530 for sites in the Site Remediation
Program (35 Ill. Adm. Code 740). A GMZ established under 35 Ill. Adm. Code
740.530 remains in effect until any condition of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 740.530(c) is
met.
i) While a GMZ established under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 740.530 is in
effect, the otherwise applicable standards of Subpart D of this Part do not apply
to the "contaminants of concern", as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code
740.120, for which groundwater remediation objectives have been approved under
35 Ill. Adm. Code 740.
j) Regardless of subsection (d), that subsection's submittal and
review requirements concerning the demonstration when corrective action is
complete do not apply to a GMZ under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 740.530. Regardless of
subsection (e), that subsection's submittal and review requirements concerning
the on-going adequacy of controls and management do not apply to groundwater
within a three-dimensional region formerly encompassed by a GMZ established under
35 Ill. Adm. Code 740.530 while a No Further Remediation Letter issued under 35
Ill. Adm. Code 740 is in effect.
k) The
Agency must develop and maintain a list of all GMZs that have not been
terminated. The list must identify the location of each GMZ. On its website
(https://epa.illinois.gov), the Agency must post the list and, at least
annually, update it. In addition, at least annually, the Agency must submit the
list to the Board for publication in the Environmental Register.
l) In
groundwater regulated under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 845, a GMZ is not available to
address any exceedance of a groundwater protection standard specified in 35
Ill. Adm. Code 845.600(a) or (b) (see 35 Ill. Adm. Code 845.600(c)).
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill. Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.260
Reclassification of Groundwater by Adjusted Standard
Any person may petition the
Board for an adjusted standard to reclassify a groundwater under Section 28.1
of the Act and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 104.Subpart D. In any proceeding to
reclassify specific groundwater by adjusted standard, in addition to complying
with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 104.406 and Section 28.1(c) of the Act, the petition must
contain information to allow the Board to determine:
a) The specific groundwater for which reclassification is
requested, including geographical extent of any aquifers, depth of groundwater,
and rate and direction of groundwater flow, and that the specific groundwater
exhibits the characteristics of the requested class specified in Section
620.210(b), 620.220(b), 620.230, or 620.240;
b) Whether the proposed change or use restriction is necessary
for economic or social development, including information concerning any
negative economic or social impacts of compliance with the currently applicable
groundwater quality standards (e.g., job losses, facility closings), as well as
an economic analysis contrasting the costs of meeting the current standards
with cost savings due to health and environmental benefits resulting from
compliance with those standards;
c) Existing and anticipated uses of the specific groundwater;
d) Existing and anticipated quality of the specific groundwater;
e) Existing and anticipated contamination, if any, of the
specific groundwater;
f) Technical feasibility and economic reasonableness of
eliminating or reducing contamination of the specific groundwater or of
maintaining existing water quality;
g) The anticipated time period over which contaminants will
continue to affect the specific groundwater;
h) Existing and anticipated impact on any potable water supplies
due to contamination;
i) Availability and cost of alternate water sources or of
treatment for users adversely affected;
j) Negative or positive effect on property values; and
k) For special resource groundwater, negative or positive effect
on:
1) The quality of surface waters; and
2) Wetlands, natural areas, and the life contained in wetlands
and natural areas, including endangered or threatened species of plant, fish,
or wildlife listed under the Endangered Species Act, 16 U.S.C. 1531 et seq., or
the Illinois Endangered Species Protection Act [520 ILCS 10].
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill. Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.301 General
Prohibition Against Use Impairment of Resource Groundwater
a) A person must not cause, threaten, or allow the release of any
contaminant to a resource groundwater such that:
1) Treatment or additional treatment is necessary to continue an
existing use or to assure a potential use of the groundwater; or
2) An existing or potential use of the groundwater is precluded.
b) Nothing in this Section prevents the establishment of a
groundwater management zone under Section 620.250 or a cumulative impact area
within a permitted site.
c) Nothing in this Section limits underground injection in
compliance with an underground injection control program administered by the
Agency under the Act, by the Department of Natural Resources, Office of Mines
and Minerals under the Illinois Oil and Gas Act (225 ILCS 725), or by USEPA
under the federal UIC regulations [40 CFR 144].
d) Nothing in this Section limits the Board from promulgating
nondegradation provisions applicable to types of facilities or activities that
impact groundwater, including landfills regulated under 35 Ill. Adm. Code:
Subtitle G.
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill. Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.302
Applicability of Preventive Notification and Preventive Response Activities
a) Preventive notification and preventive response activities, as
specified in Sections 620.305 through 620.310, apply to:
1) Class I groundwater under Section 620.210(a)(1), (a)(2),
(a)(3), (a)(5), or (a)(6) that is monitored by any person specified in
subsection (b); and
2) Class III groundwater that is monitored by any person
specified in subsection (b).
b) For subsection (a), the persons that conduct groundwater
monitoring are:
1) An owner or operator of a regulated entity required to perform
groundwater quality monitoring under State or federal law or regulation;
2) An owner or operator of a public water supply well who
conducts groundwater quality monitoring;
3) A State agency that is authorized to conduct, or is the
recipient of, groundwater quality monitoring data (e.g., Illinois Environmental
Protection Agency, Department of Public Health, Department of Agriculture,
Office of State Fire Marshal, or Department of Natural Resources); or
4) An owner or operator of a facility that conducts groundwater
quality monitoring under State or federal judicial or administrative order.
c) If a contaminant exceeds a standard specified in Section 620.410
or Section 620.430, the appropriate remedy is corrective action and Sections
620.305 and 620.310 do not apply.
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill.
Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.305 Preventive
Notification Procedures
a) For groundwater quality monitoring under Section 620.302, a
preventive notification must occur whenever a contaminant:
1) Specified in Section 620.310(a)(3)(A) is detected (except due
to natural causes) in Class I groundwater;
2) Denoted as a carcinogen under Section 620.410(b) is detected in
Class I groundwater; or
3) Subject to a standard under Section 620.430 is detected
(except due to natural causes) in Class III groundwater.
b) When a preventive notification is required for groundwater that
is monitored by a regulated entity for the subject contaminant, the owner or
operator of the site must:
1) Confirm the detection by resampling the monitoring well within
30 days after the date on which the first sample analyses are received; and
2) Provide a preventive notification to the appropriate
regulatory agency of the results of the resampling analysis within 30 days after
the date on which the sample analyses are received, but no later than 90 days
after the results of the first samples were received.
c) When a preventive notification is required for groundwater that
is monitored by a regulatory agency, the agency must notify the owner or
operator of the site where the detection has occurred. The owner or operator must:
1) Confirm the detection by resampling within 30 days after the
date of the notice by the regulatory agency; and
2) Provide preventive notification to the regulatory agency of
the results of the resampling analysis within 30 days after the date on which
the sample analyses are received, but no later than 90 days after the results
of the first samples were received.
d) When a preventive notification of a confirmed detection has
been provided by an owner or operator under this Section, additional detections
of the same contaminant do not require further notice if the groundwater
quality conditions are substantially unchanged or that preventive response is
underway for the contaminant.
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill. Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.310 Preventive
Response Activities
a) The following preventive assessment must be undertaken:
1) If a preventive notification under Section 620.305(c) is
provided by a community water supply:
A) The Agency must notify the owner or operator of any identified
potential primary source, potential secondary source, potential route, or
community water supply well that is within 2,500 feet of the wellhead.
B) The owner or operator notified under subsection (a)(1)(A) must,
within 30 days after the date of issuance of that notice, sample each water
well or monitoring well for the contaminant identified in the notice if the
contaminant or material containing the contaminant is or has been stored,
disposed of, or otherwise handled at the site. If a contaminant identified
under Section 620.305(a) is detected, then the well must be resampled within 30
days after the date on which the first sample results are received. If a
contaminant identified under Section 620.305(a) is detected by the resampling,
preventive notification must be given as specified in Section 620.305.
C) If the Agency receives analytical results under subsection
(a)(1)(B) that show a contaminant identified under Section 620.305(a) has been
detected, the Agency must:
i) Conduct a well site survey under Section 17.1(d) of the Act [415
ILCS 5/17.1(d)] if one has not been conducted within the last 5 years; and
ii) Identify those sites or activities that represent a hazard to
the continued availability of groundwaters for public use unless a groundwater
protection needs assessment has been prepared under Section 17.1(d) of the Act.
2) If a preventive notification is provided under Section
620.305(c) by a non-community water supply or for multiple private water supply
wells, the Department of Public Health must conduct a sanitary survey within
1,000 feet of the wellhead of a non-community water supply or within 500 feet
of the wellheads for multiple private water supply wells.
3) If a preventive notification under Section 620.305(b) is
provided by the owner or operator of a regulated entity and the applicable
standard of Subpart D has not been exceeded, the appropriate regulatory agency
must:
A) Determine if any of the following occurs for Class I: Potable
Resource Groundwater:
i) The levels specified below are exceeded or are changed for
pH:
|
CASRN
|
Constituent
|
Criteria (mg/L)
|
|
|
|
|
95-50-1
|
o-Dichlorobenzene
(1,2-dichlorobenzene)
|
0.01
|
|
1634-04-4
|
MTBE methyl tertiary butyl ether
|
0.02
|
|
108-95-2
|
Phenols
|
0.001
|
|
100-42-5
|
Styrene
|
0.01
|
|
108-88-3
|
Toluene
|
0.04
|
|
1330-20-7
|
Xylenes
|
0.02
|
ii) A statistically significant increase occurs above background
(as determined under other regulatory procedures (e.g., 35 Ill. Adm. Code 616,
724, 725, or 811)) for the following inorganic constituents (except due to
natural causes) or organic constituents:
|
CASRN
Inorganics
|
Constituent
|
|
7429-90-5
|
Aluminum
|
|
7440-38-2
|
Arsenic
|
|
7440-41-7
|
Beryllium
|
|
7440-43-9
|
Cadmium
|
|
7440-47-3
|
Chromium (total)
|
|
143-33-9
|
Cyanide
|
|
7439-92-1
|
Lead
|
|
7487-94-7
|
Mercury (mercuric chloride)
|
|
7439-98-7
|
Molybdenum
|
|
7440-28-0
|
Thallium
|
|
7440-62-2
|
Vanadium
|
|
Organics
|
|
|
83-32-9
|
Acenaphthene
|
|
67-64-1
|
Acetone
|
|
116-06-3
|
Aldicarb
|
|
120-12-7
|
Anthracene
|
|
319-84-6
|
alpha-BHC (alpha-benzene
hexachloride)
|
|
1912-24-9
|
Atrazine and metabolites DEA,
DIA, DACT
|
|
71-43-2
|
Benzene
|
|
56-55-3
|
Benzo(a)anthracene
|
|
205-99-2
|
Benzo(b)fluoranthene
|
|
207-08-9
|
Benzo(k)fluoranthene
|
|
50-32-8
|
Benzo(a)pyrene
|
|
65-85-0
|
Benzoic acid
|
|
78-93-3
|
2-Butanone (methyl ethyl
ketone)
|
|
1563-66-2
|
Carbofuran
|
|
75-15-0
|
Carbon disulfide
|
|
56-23-5
|
Carbon tetrachloride
|
|
12789-03-6
|
Chlordane
|
|
108-90-7
|
Chlorobenzene
|
|
67-66-3
|
Chloroform
|
|
218-01-9
|
Chrysene
|
|
94-75-7
|
2.4-D (2.4-dichlorophenoxy acetic
acid)
|
|
75-99-0
|
Dalapon
|
|
96-12-8
|
1,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane (dibromochloroorooane)
|
|
1918-00-9
|
Dicamba
|
|
106-46-7
|
p-Dichlorobenzene
(1,4-dichlorobenzene)
|
|
75-71-8
|
Dichlorodifluoromethane
|
|
75-34-3
|
1,1-Dichloroethane
|
|
75-35-4
|
1,1-Dichloroethylene
|
|
107-06-2
|
1,2-Dichloroethane
|
|
156-59-2
|
cis-1,2-Dichloroethylene
|
|
156-60-5
|
trans-1,2-Dichloroethylene
|
|
75-09-2
|
Dichloromethane (methylene
|
|
78-87-5
|
1,2-Dichloropropane
|
|
117-81-7
|
Di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate
|
|
84-66-2
|
Diethyl phthalate
|
|
84-74-2
|
Di-n-butyl phthalate
|
|
99-65-0
|
1,3-Dinitrobenzene
|
|
121-14-2
|
2,4-Dinitrotoluene
|
|
88-85-7
|
Dinoseb
|
|
123-91-1
|
1,4-Dioxane (p dioxane)
|
|
145-73-3
|
Endothall
|
|
72-20-8
|
Endrin
|
|
100-41-4
|
Ethylbenzene
|
|
106-93-4
|
Ethylene dibromide (1,2-dibromoethane)
|
|
206-44-0
|
Fluoranthene
|
|
86-73-7
|
Fluorene
|
|
58-89-9
|
gamma-HCH (gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane
lindane)
|
|
13252-13-6
|
HFPO-DA (hexafluoropropylene oxide
dimer acid, GenX)
|
|
2691-41-0
|
HMX
(octahydro-1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetrazocine)
|
|
76-44-8
|
Heptachlor
|
|
1024-57-3
|
Heptachlor epoxide
|
|
77-47-4
|
Hexachlorocyclopentadiene
|
|
193-39-5
|
Indeno(l,2,3-c,d)pyrene
|
|
98-82-8
|
Isopropylbenzene (cumene)
|
|
72-43-5
|
Methoxychlor
|
|
90-12-0
|
1-Methylnaphthalene
|
|
91-57-6
|
2-Methylnaphthalene
|
|
95-48-7
|
2-Methylphenol (o-cresol)
|
|
91-20-3
|
Naphthalene
|
|
98-95-3
|
Nitrobenzene
|
|
1336-36-3
|
PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls
as decachloro-biphenyl)
|
|
375-73-5
|
PFBS (perfluorobutanesulfonic
acid)
|
|
355-46-4
|
PFHxS (perfluorohexanesulfonic
acid)
|
|
375-95-1
|
PFNA (perfluorononanoic acid)
|
|
335-67-1
|
PFOA (perfluorooctanoic acid)
|
|
1763-23-1
|
PFOS (perfluorooctanesulfonic acid)
|
|
87-86-5
|
Pentachlorophenol
|
|
1918-02-1
|
Picloram
|
|
129-00-0
|
Pyrene
|
|
121-82-4
|
RDX
(hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine)
|
|
122-34-9
|
Simazine
|
|
118-96-7
|
TNT (2,4,6-trinitrotoluene)
|
|
93-72-1
|
2,4,5-TP (silvex)
|
|
127-18-4
|
Tetrachloroethylene
|
|
8001-35-2
|
Toxaphene
|
|
120-82-1
|
1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene
|
|
71-55-6
|
1,1,1-Trichloroethane
|
|
79-00-5
|
1,1,2-Trichloroethane
|
|
79-01-6
|
Trichloroethylene
|
|
75-69-4
|
Trichlorotluoromethane
|
|
99-35-4
|
1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene
|
|
75-01-4
|
Vinyl chloride
|
iii) For a chemical constituent of gasoline, diesel fuel, or
heating fuel, the constituent exceeds the following:
|
Constituent
|
Criterion (mg/L)
|
|
|
|
BETX
|
0.095
|
iv) For pH, a statistically significant change occurs from
background.
B) Determine if, for Class III: Special Resource Groundwater, the
levels as determined by the Board are exceeded.
C) Consider whether the owner or operator reasonably demonstrates
that:
i) The contamination is a result of contaminants remaining in
groundwater from a prior release for which appropriate action was taken in compliance
with laws and regulations in existence at the time of the release;
ii) The source of contamination is not due to the on-site release
of contaminants; or
iii) The detection resulted from error in sampling, analysis, or
evaluation.
D) Consider actions necessary to minimize the degree and extent of
contamination.
b) The appropriate regulatory agency must determine whether a
preventive response should be undertaken based on relevant factors, including
the considerations in subsection (a)(3).
c) After completion of preventive response under the authority of
an appropriate regulatory agency, the concentration of a contaminant specified
in subsection (a)(3)(A) in groundwater may exceed 50% of the applicable
numerical standard of Subpart D if the following conditions are met:
1) The exceedance has been minimized to the extent practicable;
2) Beneficial use, as appropriate for the class of groundwater,
has been assured; and
3) Any threat to public health or the environment has been
minimized.
d) Nothing in this Section limits the authority of the State or
the United States to require or perform any corrective action process.
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill.
Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.401
Applicability
Groundwater must meet the
standards appropriate to the groundwater's class as specified in this Subpart
and the nondegradation provisions of Subpart C
(Source:
Amended at 49 Ill. Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.405 General
Prohibitions Against Violations of Groundwater Quality Standards
A person must not cause,
threaten, or allow the release of any contaminant to groundwater so as to cause
a groundwater quality standard specified in this Subpart to be exceeded.
(Source:
Amended at 49 Ill. Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.410 Groundwater
Quality Standards for Class I: Potable Resource Groundwater
a) Inorganic Chemical Constituents
Except due to
natural causes or as provided in Section 620.450, concentrations of the
following chemical constituents must not be exceeded in Class I groundwater:
|
CASRN
|
Constituent
|
Standard (mg/L) a,b
|
|
7429-90-5
|
Aluminum
|
l.9c
|
|
7440-36-0
|
Antimony
|
0.006d
|
|
7440-38-2
|
Arsenice
|
0.01d
|
|
7440-39-3
|
Barium
|
2.0d
|
|
7440-41-7
|
Beryllium
|
0.004d
|
|
7440-42-8
|
Boron
|
2.0f
|
|
7440-43-9
|
Cadmium
|
0.005d
|
|
16887-00-6
|
Chloride
|
200g
|
|
7440-47-3
|
Chromium (total)
|
0.ld
|
|
7440-48-4
|
Cobalt
|
0.0012c
|
|
7440-50-8
|
Copper
|
0.5h
|
|
143-33-9
|
Cyanide
|
0.2d
|
|
7681-49-4
|
Fluoride
|
4d
|
|
7439-89-6
|
Iron
|
5g
|
|
7439-92-1
|
Lead
|
0.0075i
|
|
7439-93-2
|
Lithium
|
0.04j
|
|
7439-96-5
|
Manganese
|
0.l5k
|
|
7487-94-7
|
Mercury (mercuric chloride)
|
0.002d
|
|
7439-98-7
|
Molybdenum
|
0.308c
|
|
7440-02-0
|
Nickel
|
0.077c
|
|
14797-55-8
|
Nitrate as N
|
10d
|
|
14797-73-0
|
Perchlorate
|
0.0081c
|
|
7440-14-4
|
Radium (combined 226+228)
|
5d
|
|
7782-49-2
|
Selenium
|
0.02f
|
|
7440-22-4
|
Silver
|
0.058c
|
|
14808-79-8
|
Sulfate
|
400g
|
|
|
TDS (total dissolved solids)
|
1,200g
|
|
7440-28-0
|
Thallium
|
0.002d
|
|
7440-62-2
|
Vanadium
|
0.00027c
|
|
7440-66-6
|
Zinc
|
l.2c
|
Constituent Name and Groundwater
Quality Standard Notations
a The
standard unit for radium (combined 226+228) is picocuries per liter (pCi/L).
b The
inorganic groundwater quality standards are based on total metal analyses for
the evaluation of human health effects.
c The
standard is calculated using the Human Threshold Toxicant Advisory
Concentration (HTTAC) procedures at Appendix A.
d The
standard is based on the Maximum Contaminant Level (MCL), promulgated by USEPA,
Office of Water, and Illinois Primary Drinking Water Standards specified in 35
Ill. Adm. Code 611.
e The
constituent meets the definition of a "carcinogen" in Section
620.110.
f The
standard is based on beneficial use for irrigation of crops, per "Water
Quality Criteria", by National Academy of Sciences, incorporated by
reference in Section 620.125.
g The
standard is the 95% confidence concentration stated in the Agency's "Integrated
Water Quality Report and Section 303(d) List", incorporated by reference in
Section 620.125.
h The
standard is based on beneficial use for watering livestock, per "Water
Quality Criteria", by National Academy of Sciences, incorporated by
reference in Section 620.125.
i The
standard is 50% of the USEPA "action level" of 0.015 mg/L for lead.
The USEPA action level applies at the service connection. The standard is
reduced by 50% as a safety margin, based on the assumption that 50% of water
would be treated.
j The
standard is the "LLOQ" or "LCMRL" as defined in Section
620.110.
k The standard is promulgated at 35 Ill. Adm. Code 611.300.
b) Organic Chemical Constituents
Except due to
natural causes or as provided in Section 620.450 or subsection (c) of this
Section, concentrations of the following organic chemical constituents must not
be exceeded in Class I groundwater:
|
CASRN
|
Constituent
|
Standard (mg/L)
|
|
83-32-9
|
Acenaphthene
|
0.23a
|
|
67-64-1
|
Acetone
|
3.5a
|
|
15972-60-8
|
Alachlorb
|
0.002c
|
|
116-06-3
|
Aldicarb
|
0.003c
|
|
120-12-7
|
Anthracene
|
1.2a
|
|
319-84-6
|
alpha-BHC (alpha-benzene
hexachloride)b
|
0.000012d
|
|
71-43-2
|
Benzeneb
|
0.005c
|
|
56-55-3
|
Benzo(a)anthracenee
|
0.00025d
|
|
205-99-2
|
Benzo(b)fluoranthenee
|
0.00025d
|
|
207-08-9
|
Benzo(k)fluoranthenee
|
0.0025d
|
|
50-32-8
|
Benzo(a)pyrenee
|
0.0002c
|
|
65-85-0
|
Benzoic acid
|
15a
|
|
78-93-3
|
2-Butanone (methyl ethyl
ketone)
|
2.3a
|
|
1563-66-2
|
Carbofuran
|
0.04c
|
|
75-15-0
|
Carbon disulfide
|
0.38a
|
|
56-23-5
|
Carbon tetrachlorideb
|
0.005c
|
|
12789-03-6
|
Chlordaneb
|
0.002c
|
|
108-90-7
|
Chlorobenzene
|
0.lc
|
|
67-66-3
|
Chloroformb
|
0.07f
|
|
218-01-9
|
Chrysenee
|
0.025d
|
|
94-75-7
|
2,4-D (2,4-dichlorophenoxy
acetic acid)
|
0.07c
|
|
75-99-0
|
Dalapon
|
0.2c
|
|
53-70-3
|
Dibenzo(a,h)anthracenee
|
0.0001g
|
|
96-12-8
|
1,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane (dibromochloropropane)e
|
0.0002c
|
|
1918-00-9
|
Dicamba
|
0.12a
|
|
95-50-1
|
o-Dichlorobenzene (1,2-dichlorobenzene)
|
0.6c
|
|
106-46-7
|
p-Dichlorobenzene (1,4-dichlorobenzene)b
|
0.075c
|
|
75-71-8
|
Dichlorodifluoromethane
|
0.77a
|
|
75-34-3
|
1,1-Dichloroethane
|
0.77a
|
|
107-06-2
|
1,2-Dichloroethaneb
|
0.005c
|
|
75-35-4
|
1,1-Dichloroethylene
|
0.007c
|
|
156-59-2
|
cis-1,2-Dichloroethylene
|
0.07c
|
|
156-60-5
|
trans-1,2-Dichloroethylene
|
0.lc
|
|
75-09-2
|
Dichloromethane (methylene
chloride)e
|
0.005c
|
|
78-87-5
|
1,2-Dichloropropaneb
|
0.005c
|
|
117-81-7
|
Di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalateb
|
0.006c
|
|
84-66-2
|
Diethyl phthalate
|
3.1a
|
|
84-74-2
|
Di-n-butyl phthalate
|
0.38a
|
|
99-65-0
|
1,3-Dinitrobenzene
|
0.001g
|
|
121-14-2
|
2,4-Dinitrotolueneb
|
0.001g
|
|
606-20-2
|
2,6-Dinitrotolueneb
|
0.0001g
|
|
88-85-7
|
Dinoseb
|
0.007c
|
|
123-91-1
|
1,4-Dioxane (p-dioxane)b
|
0.00078d
|
|
145-73-3
|
Endothall
|
0.lc
|
|
72-20-8
|
Endrin
|
0.002c
|
|
100-41-4
|
Ethylbenzeneb
|
0.7c
|
|
106-93-4
|
Ethylene dibromide (1,2-dibromoethane)b
|
0.00005c
|
|
206-44-0
|
Fluoranthene
|
0.15a
|
|
86-73-7
|
Fluorene
|
0.15a
|
|
58-89-9
|
gamma-HCH (gamma-Hexachlorocyclohexane,
lindane)b
|
0.0002c
|
|
13252-13-6
|
HFPO-DA (hexafluoropropylene
oxide dimer acid GenX)
|
0.000010c
|
|
2691-41-0
|
HMX (octahydro-1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetrazocine)
|
0.77a
|
|
76-44-8
|
Heptachlorb
|
0.0004c
|
|
1024-57-3
|
Heptachlor epoxideb
|
0.0002c
|
|
77-47-4
|
Hexachlorocyclopentadiene
|
0.05c
|
|
193-39-5
|
Indeno(l,2,3-c,d)pyrenee
|
0.00025d
|
|
98-82-8
|
Isopropylbenzene (cumene)b
|
0.38a
|
|
93-65-2
|
MCPP (mecoprop)
|
0.1g
|
|
1634-04-4
|
MTBE (methyl tertiary-butyl
ether)
|
0.038a
|
|
72-43-5
|
Methoxychlor
|
0.04c
|
|
90-12-0
|
1-Methylnaphthalene
|
0.27a
|
|
91-57-6
|
2-Methylnaphthalene
|
0.015c
|
|
95-48-7
|
2-Methylphenol (o-cresol)
|
0.19a
|
|
91-20-3
|
Naphthalene
|
0.077a
|
|
98-95-3
|
Nitrobenzene
|
0.0077a
|
|
1336-36-3
|
PCBs (polychlorinated
biphenyls as decachloro-biphenyl)b
|
0.0005c
|
|
375-73-5
|
PFBS (perfluorobutanesulfonic
acid)
|
0.002c
|
|
355-46-4
|
PFHxS (perfluorohexanesulfonic
acid)
|
0.000010c
|
|
375-95-1
|
PFNA (perfluorononanoic acid)
|
0.000010c
|
|
335-67-1
|
PFOA (perfluorooctanoic acid)b
|
0.000004bc
|
|
1763-23-1
|
PFOS (perfluorooctanesulfonic
acid)
|
0.000004bc
|
|
87-86-5
|
Pentachlorophenol
|
0.001c
|
|
108-95-2
|
Phenol
|
0.1h
|
|
1918-02-1
|
Picloram
|
0.5c
|
|
129-00-0
|
Pyrene
|
0.12a
|
|
121-82-4
|
RDX (hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine)
|
0.062a
|
|
122-34-9
|
Simazine
|
0.004c
|
|
100-42-5
|
Styrene
|
0.lc
|
|
118-96-7
|
TNT (2,4,6-trinitrotoluene)
|
0.0077a
|
|
93-72-1
|
2,4,5-TP (silvex)
|
0.05c
|
|
127-18-4
|
Tetrachloroethyleneb
|
0.005c
|
|
108-88-3
|
Toluene
|
1c
|
|
8001-35-2
|
Toxapheneb
|
0.003c
|
|
120-82-1
|
1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene
|
0.07c
|
|
71-55-6
|
1,1,1-Trichloroethane
|
0.2c
|
|
79-00-5
|
1,1,2-Trichloroethane
|
0.005c
|
|
79-01-6
|
Trichloroethylenee
|
0.005c
|
|
75-69-4
|
Trichlorofluoromethane
|
1.2a
|
|
99-35-4
|
1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene
|
0.46a
|
|
75-01-4
|
Vinyl chloridee
|
0.002c
|
|
1330-20-7
|
Xylenes
|
10c
|
Constituent Name and Groundwater
Quality Standard Notations
a The
standard is the Human Threshold Toxicant Advisory Concentration (HTTAC),
calculated using procedures specified in Appendix A.
b The
constituent meets the definition of a "carcinogen" in Section
620.110.
c The
standard is based on the Maximum Contaminant Level (MCL), promulgated by USEPA,
Office of Water, and Illinois Primary Drinking Water Standards in 35 Ill. Adm.
Code 611.
d The
standard is the Human Nonthreshold Toxicant Advisory Concentration
("HNTAC"), calculated using procedures specified in Appendix A.
e The
constituent meets the definition of a "mutagen" in Section 620.110.
f The
standard is based on the Maximum Contaminant Level Goal ("MCLG"),
promulgated by USEPA, Office of Water.
g The
standard is the "LLOQ" or "LCMRL" as defined in Section
620.110.
h The
standard is based on 35 Ill. Adm. Code 302.208.
c) Complex Organic Chemical Mixtures
1) Concentrations of the following chemical constituents must not
be exceeded in Class I groundwater:
|
CASRN
|
Constituent
|
Standard (mg/L)
|
|
71-43-2
|
Benzenea
|
0.005b
|
|
|
Total BETX
|
11.705c
|
Constituent Name and Groundwater
Quality Standard Notations
a The
constituent meets the definition of a "carcinogen" in Section
620.110.
b The
standard is based on the Maximum Contaminant Level (MCL), promulgated by USEPA,
Office of Water, and Illinois Primary Drinking Water Standards at 35 Ill. Adm.
Code 611.
c The
standard is the total combined standard of benzene, ethylbenzene, toluene, and
xylenes.
2) Atrazine
and Metabolites
Concentrations of the following
chemical constituents must not be exceeded in Class I groundwater.
|
CASRN
|
Constituent
|
Standard (mg/L)
|
|
1912-24-9
|
Atrazine
|
0.003a
|
|
|
Total Atrazine and Metabolites
|
0.003
|
|
6190-65-4
|
DEA (desethyl-atrazine)
|
|
|
1007-28-9
|
DIA (desisopropyl-atrazine)
|
|
|
3397-62-4
|
DACT (diaminochlorotriazine)
|
|
Groundwater Quality Standard
Notation
a The standard is based on the Maximum Contaminant Level
(MCL), promulgated by USEPA, Office of Water, and Illinois Primary Drinking
Water Standards at 35 Ill. Adm. Code 611.
d) pH
Except due to
natural causes, a pH range of 6.5 - 9.0 units must not be exceeded in Class I
groundwater.
e) Beta Particle and Photon Radioactivity
1) Except due to natural causes, the average annual concentration
of beta particle and photon radioactivity from man-made radionuclides must not
exceed a dose equivalent to the total body or any internal organ greater than 4
mrem/year in Class I groundwater. If two or more radionuclides are present, the
sum of their dose equivalent to the total body or any internal organ must not
exceed 4 mrem/year in Class I groundwater except due to natural causes.
2) Except for the radionuclides specified in subsection (e)(3),
the concentration of man-made radionuclides causing 4 mrem total body or organ
dose equivalent must be calculated on the basis of a 2 liter per day drinking
water intake using the 168-hour data in compliance with the procedure specified
in NCRP Report Number 22, incorporated by reference in Section 620.125(a).
3) Except due to natural causes, the average annual concentration
assumed to produce a total body or organ dose of 4 mrem/year of the following
chemical constituents must not be exceeded in Class I groundwater:
|
CASRN
|
Constituent
|
Critical Organ
|
Standard (pCi/L)
|
|
10028-17-8
|
Tritium
|
Total Body
|
20,000
|
|
10098-97-2
|
Strontium-90
|
Bone Marrow
|
8.0
|
f) No
facility that is subject to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 811 or 814 must comply with any
requirement or standard of those rules to the extent it incorporates or is
otherwise based on any of the following constituents or their standards under
this Section:
|
CASRN
|
Constituent
|
|
13252-13-6
|
HFPO-DA (hexafluoropropylene
oxide dimer acid GenX)
|
|
375-73-5
|
PFBS (perfluorobutanesulfonic
acid)
|
|
355-46-4
|
PFHxS (perfluorohexanesulfonic
acid)
|
|
375-95-1
|
PFNA (perfluorononanoic acid)
|
|
335-67-1
|
PFOA (perfluorooctanoic acid)
|
|
1763-23-1
|
PFOS (perfluorooctanesulfonic
acid)
|
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill.
Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.420 Groundwater
Quality Standards for Class II: General Resource Groundwater
a) Inorganic Chemical Constituents
1) Except due to natural causes or as provided in Section 620.450
or subsection (a)(3) or (e) of this Section, concentrations of the following
chemical constituents must not be exceeded in Class II groundwater:
|
CASRN
|
Constituent
|
Standard (mg/L)a
|
|
7440-36-0
|
Antimony
|
0.024b
|
|
7440-38-2
|
Arsenicb
|
0.2d
|
|
7440-39-3
|
Barium
|
2.0e
|
|
7440-41-7
|
Beryllium
|
0.5f
|
|
7440-43-9
|
Cadmium
|
0.05g
|
|
7440-47-3
|
Chromium (total)
|
1.0g
|
|
7440-48-4
|
Cobalt
|
1d
|
|
143-33-9
|
Cyanide
|
0.6d
|
|
7681-49-4
|
Fluoride
|
4e
|
|
7439-92-1
|
Lead
|
1.0d
|
|
7439-93-2
|
Lithium
|
2.5f
|
|
7487-94-7
|
Mercury (mercuric chloride)
|
0.01d
|
|
7439-98-7
|
Molybdenum
|
0.308e
|
|
14797-55-8
|
Nitrate as N
|
100d
|
|
14797-73-0
|
Perchlorate
|
0.0081e
|
|
7440-28-0
|
Thallium
|
0.02h
|
|
7440-62-2
|
Vanadium
|
0.1d
|
Constituent Name and Groundwater Quality Standard
Notations
a The inorganic groundwater quality standards are based
on total metal analyses for the evaluation of human health effects.
b A treatment factor of 4 is applied to the Class I
groundwater quality standard. The constituent's treatment efficiency is based
on the effectiveness to treat the constituent in the groundwater at an 75%
removal efficiency rate for the constituent.
c The constituent meets the definition of a
"carcinogen" in Section 620.110.
d The standard is based on beneficial use for watering
livestock, per "Water Quality Criteria", by National Academy of
Sciences, incorporated by reference in Section 620.125.
e The Class II standard is equal to the Class I
groundwater quality standard.
f The standard is based on beneficial use for irrigation
of crops, per "Water Quality Criteria", by National Academy of
Sciences, incorporated by reference in Section 620.125.
g The standard is based on beneficial use for watering
livestock and irrigation of crops, per "Water Quality Criteria", by
National Academy of Sciences, incorporated by reference in Section 620.125.
h A treatment factor of 10 is applied to the Class I
groundwater quality standard. The constituent's treatment efficiency is based
on the effectiveness to treat the constituent in the groundwater at an 90%
removal efficiency rate for the constituent.
2) Except as provided in Section 620.450 or subsection (a)(3) or (e)
of this Section, concentrations of the following chemical constituents must not
be exceeded in Class II groundwater:
|
CASRN
|
Constituent
|
Standard (mg/L)a,b
|
|
7429-90-5
|
Aluminum
|
5c
|
|
7440-42-8
|
Boron
|
2d
|
|
16887-00-6
|
Chloride
|
200e
|
|
7440-50-8
|
Copper
|
0.5c
|
|
7439-89-6
|
Iron
|
5e
|
|
7439-96-5
|
Manganese
|
10d
|
|
7440-02-0
|
Nickel
|
2d
|
|
7440-14-4
|
Radium (combined 226+228)
|
5f
|
|
7782-49-2
|
Selenium
|
0.02d
|
|
7440-22-4
|
Silver
|
0.058f
|
|
14808-79-8
|
Sulfate
|
400e
|
|
|
TDS (total dissolved solids)
|
1,200e
|
|
7440-66-6
|
Zinc
|
10d
|
Constituent
Name and Groundwater Quality Standard Notations
a The
standard units for radium (combined 226+228) is picocuries per liter (pCi/L).
b The
inorganic groundwater quality standards are based on total metal analyses for
the evaluation of human health effects.
c The
standard is based on beneficial use for watering livestock and irrigation of
crops, per "Water Quality Criteria", by National Academy of Sciences,
incorporated by reference in Section 620.125.
d The
standard is based on beneficial use for irrigation of crops, per "Water
Quality Criteria", by National Academy of Sciences, incorporated by
reference in Section 620.125.
e The
standard is the 95% confidence concentration stated in the Agency's "Integrated
Water Quality Report and Section 303(d) List", incorporated by reference in
Section 620.125.
f The Class II standard is equal to the Class I groundwater
quality standard.
3) The standard for any inorganic chemical constituent specified
in subsection (a)(2) and barium specified in subsection (a)(1) does not apply
within fill material or within the upper 10 feet of parent material under fill
material on a site not within the rural property class for which the conditions
of subsection (a)(3)(A) or (a)(3)(B) are met. For pH, the standard specified in subsection (d) does not apply to
groundwater within fill material below 5 feet of land surface or within the
upper 10 feet of parent material under fill material on a site not within the
rural property class for which the conditions of subsection (a)(3)(A) or
(a)(3)(B) are met.
A) Before November 25, 1991, surficial characteristics have been
altered by placing the fill material so as to impact the concentration of any
parameter (constituent or pH) specified in this subsection (a)(3), and any
on-site groundwater monitoring of the parameter is available for review by the
Agency.
B) On November 25, 1991, surficial characteristics are in the
process of being altered by placing the fill material, in a reasonably
continuous manner to completion, so as to impact the concentration of any
parameter (constituent or pH) specified in this subsection (a)(3), and any
on-site groundwater monitoring of the parameter is available for review by the
Agency.
4) For subsection (a)(3), the term "fill material"
means clean earthen materials, slag, ash, clean demolition debris, or similar
materials.
b) Organic Chemical Constituents
1) Except due to natural causes or as provided in Section 620.450
or subsection (b)(2) or (e) of this Section, concentrations of the following
organic chemical constituents must not be exceeded in Class II groundwater:
|
CASRN
|
Constituent
|
Standard (mg/L)
|
|
83-32-9
|
Acenaphthene
|
1.2a
|
|
67-64-1
|
Acetone
|
3.5b
|
|
15972-60-8
|
Alachlorc
|
0.01a
|
|
116-06-3
|
Aldicarb
|
0.015a
|
|
120-12-7
|
Anthracene
|
6a
|
|
319-84-6
|
alpha-BHC (alpha-benzenehexachloride)c
|
0.00006a
|
|
71-43-2
|
Benzenec
|
0.025a
|
|
56-55-3
|
Benzo(a)anthracened
|
0.0012a
|
|
205-99-2
|
Benzo(b)fluoranthened
|
0.0012a
|
|
207-08-9
|
Benzo(k)fluoranthened
|
0.012a
|
|
50-32-8
|
Benzo(a)pyrened
|
0.002e
|
|
65-85-0
|
Benzoic acid
|
15b
|
|
78-93-3
|
2-Butanone (methyl ethyl
ketone)
|
2.3b
|
|
1563-66-2
|
Carbofuran
|
0.2a
|
|
75-15-0
|
Carbon disulfide
|
1.9a
|
|
56-23-5
|
Carbon tetrachloridec
|
0.025a
|
|
12789-03-6
|
Chlordanec
|
0.01a
|
|
108-90-7
|
Chlorobenzene
|
0.5a
|
|
67-66-3
|
Chloroformc
|
0.35a
|
|
218-01-9
|
Chrysened
|
0.12a
|
|
94-75-7
|
2,4-D (2,4-dichloroohenoxy
acetic acid)
|
0.35a
|
|
75-99-0
|
Dalapon
|
2.0e
|
|
53-70-3
|
Dibenzo(a,h)anthracened
|
0.0005a
|
|
96-12-8
|
1,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropaned
|
0.002e
|
|
1918-00-9
|
Dicamba
|
0.12b
|
|
95-50-1
|
o-Dichlorobenzene (1,2-dichlorobenzene)
|
1.5f
|
|
106-46-7
|
p-Dichlorobenzene
(1,4-dichlorobenzene)c
|
0.375a
|
|
75-71-8
|
Dichlorodifluoromethane
|
3.9a
|
|
75-34-3
|
1,1-Dichloroethane
|
3.9a
|
|
107-06-2
|
1,2-Dichloroethanec
|
0.025a
|
|
75-35-4
|
1,1-Dichloroethylene
|
0.035a
|
|
156-59-2
|
cis-1,2-Dichloroethylene
|
0.2g
|
|
156-60-5
|
trans-1,2-Dichloroethylene
|
0.5a
|
|
75-09-2
|
Dichloromethane (methylene
chloride)d
|
0.025a
|
|
78-87-5
|
1,2-Dichloropropaneb
|
0.025a
|
|
117-81-7
|
Di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalateb
|
0.06e
|
|
84-66-2
|
Diethyl phthalate
|
3.1b
|
|
84-74-2
|
Di-n-butyl phthalate
|
1.9a
|
|
99-65-0
|
1,3-Dinitrobenzene
|
0.001b
|
|
121-14-2
|
2,4-Dinitrotoluenec
|
0.005a
|
|
606-20-2
|
2,6-Dinitrotoluenec
|
0.005a
|
|
88-85-7
|
Dinoseb
|
0.07e
|
|
123-91-1
|
1,4-Dioxane (p-dioxane)c
|
0.00078b
|
|
145-73-3
|
Endothall
|
0.1b
|
|
72-20-8
|
Endrin
|
0.01a
|
|
100-41-4
|
Ethylbenzenec
|
1.0h
|
|
106-93-4
|
Ethylene dibromide (1,2-dibromoethane)c
|
0.0005e
|
|
206-44-0
|
Fluoranthene
|
0.75a
|
|
86-73-7
|
Fluorene
|
0.75a
|
|
58-89-9
|
gamma-HCH (gamma-
hexachlorocyclohexane, lindane)c
|
0.001a
|
|
13252-13-6
|
HFPO-DA (hexafluoropropylene
oxide dimer acid GenX)
|
0.000010b
|
|
2691-41-0
|
HMX (octahydro-1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetrazocine)
|
3.9a
|
|
76-44-8
|
Heptachlorc
|
0.002a
|
|
1024-57-3
|
Heptachlor epoxidec
|
0.001a
|
|
77-47-4
|
Hexachlorocyclopentadiene
|
0.5e
|
|
193-39-5
|
Indeno(1,2,3-c,d)pyrened
|
0.0012a
|
|
98-82-8
|
Isopropylbenzene (cumene)c
|
1.9a
|
|
93-65-2
|
MCPP (mecoprop)
|
0.1b
|
|
1634-04-4
|
MTBE (methyl tertiary-butyl
ether)
|
0.5e
|
|
72-43-5
|
Methoxychlor
|
0.2a
|
|
90-12-0
|
1-Methylnaphthalene
|
1.35a
|
|
91-57-6
|
2-Methylnaphthalene
|
0.075a
|
|
95-48-7
|
2-Methylphenol (o-cresol)
|
0.19b
|
|
91-20-3
|
Naphthalene
|
0.39a
|
|
98-95-3
|
Nitrobenzene
|
0.0077b
|
|
1336-36-3
|
PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls
as decachloro- biphenyl)c
|
0.0025a
|
|
375-73-5
|
PFBS (perfluorobutanesulfonic
acid)
|
0.002b
|
|
355-46-4
|
PFHxS (perfluorohexanesulfonic
acid)
|
0.000010b
|
|
375-95-1
|
PFNA (perfluorononanoic acid)
|
0.000010b
|
|
335-67-1
|
PFOA (perfluorooctanoic acid)c
|
0.000004b
|
|
1763-23-1
|
PFOS (perfluorooctanesulfonic
acid)c
|
0.000004b
|
|
87-86-5
|
Pentachlorophenol
|
0.005a
|
|
108-95-2
|
Phenol
|
0.1ii
|
|
1918-02-1
|
Picloram
|
5.0e
|
|
129-00-0
|
Pyrene
|
0.6a
|
|
121-82-4
|
RDX (hexahydro-l,3,5-trinitro-l,3,5-trianzine)
|
0.062b
|
|
122-34-9
|
Simazine
|
0.04e
|
|
100-42-5
|
Styrene
|
0.5a
|
|
118-96-7
|
TNT (2,4,6-trinitrotoluene)
|
0.039a
|
|
93-72-1
|
2,4,5-TP (silvex)
|
0.25a
|
|
127-18-4
|
Tetrachloroethylenec
|
0.025a
|
|
108-88-3
|
Toluene
|
2.5f
|
|
8001-35-2
|
Toxaphenec
|
0.015a
|
|
120-82-1
|
1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene
|
0.7e
|
|
71-55-6
|
1,1,1-Trichloroethane
|
1a
|
|
79-00-5
|
1,1,2-Trichloroethane
|
0.05e
|
|
79-01-6
|
Trichloroethylened
|
0.025a
|
|
75-69-4
|
Trichlorofluoromethane
|
6a
|
|
99-35-4
|
1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene
|
2.3a
|
|
75-01-4
|
Vinyl chlorided
|
0.01a
|
|
1330-20-7
|
Xylenes
|
10b
|
Constituent Name and Groundwater
Quality Standard Notations
a A
treatment factor of 5 is applied to the Class I groundwater quality standard.
The constituent's treatment efficiency is based on the effectiveness to treat
the constituent in the groundwater at an 80% removal efficiency rate for the
constituent.
b The
Agency's treatment efficiency determination demonstrates a treatment factor is
not applicable for the constituent. The standard is equal to the Class I
groundwater quality standard.
c The
constituent meets the definition of a "carcinogen" in Section
620.110.
d The
constituent meets the definition of a "mutagen" in Section 620.110.
e A
treatment factor of 10 is applied to the Class I groundwater quality standard.
The constituent's treatment efficiency is based on the effectiveness to treat
the constituent in the groundwater at a 90% removal efficiency rate for the
constituent.
f A
treatment factor of 2.5 is applied to the Class I groundwater quality
standard. The constituent's treatment efficiency is based on the effectiveness
to treat the constituent in the groundwater at a 60% removal efficiency rate
for the constituent.
g A
treatment factor of 3 is applied to the Class I groundwater quality standard.
The constituent's treatment efficiency is based on the effectiveness to treat
the constituent in the groundwater at a 65% removal efficiency rate for the
constituent.
h A
treatment factor of 1.5 is applied to the Class I groundwater quality
standard. The constituent's treatment efficiency is based on the effectiveness
to treat the constituent in the groundwater at a 30% removal efficiency rate
for the constituent.
i The standard is based on 35 Ill. Adm. Code 302.208.
2) The standards for pesticide chemical constituents specified in
subsection (b)(1) do not apply to groundwater within 10 feet of the land
surface if the concentrations of the constituents result from applying
pesticides in a manner consistent with the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and
Rodenticide Act (7 U.S.C. 136 et seq.) and the Illinois Pesticide Act [415 ILCS
60].
c) Complex Organic Chemical Mixtures
1) Concentrations of the following organic chemical constituents
must not be exceeded in Class II groundwater:
|
CASRN
|
Constituent
|
Standard (mg/L)
|
|
71-43-2
|
Benzenea
|
0.025b
|
|
|
Total BETX
|
13.525c
|
Constituent Name and Groundwater
Quality Standard Notations
a The
constituent meets the definition of a "carcinogen" in Section
620.110.
b A
treatment factor of 5 is applied to the Class I groundwater quality standard.
The constituent's treatment efficiency is based on the effectiveness to treat
the constituent in the groundwater at an 80% removal efficiency rate for the
constituent.
c The standard is the total combined Class II standard of
benzene, ethylbenzene, toluene, and xylenes.
2) Atrazine
and Metabolites
Concentration of the following
chemical constituents must not be exceeded in Class II groundwater.
|
CASRN
|
Constituent
|
Standard (mg/L)
|
|
1912-24-9
|
Atrazine
|
0.015a
|
|
|
Total Atrazine and Metabolites
|
0.015
|
|
6190-65-4
|
DEA (desethyl-atrazine)
|
|
|
1007-28-9
|
DIA (desisopropyl-atrazine)
|
|
|
3397-62-4
|
DACT (diaminochlorotriazine)
|
|
Constituent Name and Groundwater
Quality Standard Notations:
a A treatment factor of 5 is applied to the Class I
groundwater quality standard. The constituent's treatment efficiency is based
on the effectiveness to treat the constituent in the groundwater at an 80%
removal efficiency rate for the constituent.
d) pH
Except due to
natural causes, a pH range of 6.5 - 9.0 units must not be exceeded in Class II
groundwater.
e) No
facility that is subject to 35 Ill. Adm. Code 811 or 814 must comply with any
requirement or standard of those rules to the extent it incorporates or is
otherwise based on any of the following constituents or their standards under
this Section:
|
CASRN
|
Constituent
|
|
13252-13-6
|
HFPO-DA
(hexafluoropropylene oxide
dimer acid GenX)
|
|
375-73-5
|
PFBS
(perfluorobutanesulfonic acid)
|
|
355-46-4
|
PFHxS
(perfluorohexanesulfonic acid)
|
|
375-95-1
|
PFNA (perfluorononanoic acid)
|
|
335-67-1
|
PFOA (perfluorooctanoic acid)
|
|
1763-23-1
|
PFOS
(perfluorooctanesulfonic acid)
|
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill.
Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.430 Groundwater
Quality Standards for Class III: Special Resource Groundwater
Except due to natural causes,
concentrations of inorganic and organic chemical constituents and ranges of pH
must not exceed the standards specified in Section 620.410. This prohibition
does not apply to:
a) Chemical constituents for which the Board has adopted standards
under Section 620.260; or
b) Class
III Special Resource Groundwater established under Section 620.230(b) and
depicted in the Environmental Register, but only at the dedicated nature
preserves identified in this subsection (b), and only for the conditions at
those preserves for which standards are specified in this subsection (b).
1) The
following standards apply for Pautler Cave Nature Preserve and Stemler Cave
Nature Preserve (Environmental Register, May 2005, No. 611), Fogelpole Cave
Nature Preserve (Environmental Register, May 2003, No. 587), and Armin Krueger
Speleological Nature Preserve (Environmental Register, December 2009, No. 666):
|
Chloride
|
20 mg/L
|
|
pH
|
range of 7.0-9.0 Standard Units
|
2) The
following standard applies for Cotton Creek Marsh Nature Preserve and Spring
Grove Fen Nature Preserve (Environmental Register, July 2012, No. 697):
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill. Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.440 Groundwater
Quality Standards for Class IV: Other Groundwater
a) Except as provided in subsection (b), (c), (d), or (e) Class
IV: Other Groundwater standards are equal to the existing concentrations of
constituents in groundwater.
b) For groundwater within a zone of attenuation as defined in 35
Ill. Adm. Code 810.103 and determined in compliance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 811.320(c),
the standards specified in Section 620.420 must not be exceeded. This
prohibition does not apply to any concentrations of contaminants within
leachate released from a permitted unit.
c) For groundwater within a previously mined area, the standards specified
in Section 620.420 must not be exceeded, except the standards are the existing
concentrations for TDS, chloride, iron, manganese, sulfates, pH,
1,3-dinitrobenzene, 2,4-dinitrotoluene, 2,6-dinitrotoluene, HMX (octahydro-1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetrazocine),
nitrobenzene, RDX (hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine royal),
1,3,5-trinitrobenzene, and TNT (2,4,6-trinitrotoluene).
d) For
groundwater regulated under Part 845, the groundwater protection standard
(GWPS) under Section 845.600 must not be exceeded for any constituent with a
GWPS under Section 845.600. For any constituent that does not have a GWPS under
Section 845.600, the groundwater quality standards (GWQS) of Sections 620.410,
620.420, 620.430 or 620.440(b) and (c) apply.
e) Nothing
in this Section limits underground injection in compliance with an underground
injection control program administered by the Agency under the Act, by the
Department of Natural Resources, Office of Oil and Gas Resource Management
under the Illinois Oil and Gas Act [225 ILCS 725], or by USEPA under the
federal UIC regulations [40 CFR 144].
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill.
Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.450 Alternative
Groundwater Quality Standards
a) Groundwater Quality Restoration Standards
1) Subsections (a)(3) and (a)(4)(B) apply to all released
chemical constituents in groundwater within a groundwater management zone (GMZ)
that are the subject of the GMZ approved under Section 620.250(c)(2).
2) Subsection (a)(4)(A) applies to all released chemical constituents
in groundwater within a three-dimensional region formerly encompassed by a GMZ
that were the subject of the GMZ approved under Section 620.250(c)(2).
3) Before the Agency issues a written determination approving the
demonstration of the site owner or operator under Section 620.250(d)(1) or
(d)(2), none of the standards specified in Section 620.410, 620.420, 620.430, or
620.440 apply to any released chemical constituent if the owner or operator
performs and complies with the schedule for all parts of the GMZ.
4) After the Agency issues a written determination approving the
demonstration of the site owner or operator under Section 620.250(d)(1) or
(d)(2), the standard for each released chemical constituent is:
A) The standard specified in Section 620.410, 620.420, 620.430, or
620.440 if the concentration of the constituent, as determined by groundwater
monitoring, is less than or equal to the standard for the applicable class of
groundwater specified in one of those Sections; or
B) The concentration of the constituent, as determined by
groundwater monitoring, if the concentration exceeds the standard for the otherwise
applicable class of groundwater specified in Section 620.410, 620.420, 620.430,
or 620.440 and:
i) To the extent practicable, the exceedance has been minimized
and beneficial use, as appropriate for the otherwise applicable class of
groundwater, has been returned; and
ii) Any threat to public health or the environment has been
minimized.
5) The Agency must develop and maintain a list of all concentrations
derived under subsection (a)(4)(B). For each concentration, the list must
identify the location of the corresponding GMZ. On its website
(https://epa.illinois.gov), the Agency must post the list and, at least
semi-annually, update it. In addition, at least annually, the Agency must
submit the list to the Board for publication in the Environmental Register.
b) Coal Reclamation Groundwater Quality Standards
1) Any inorganic chemical constituent or pH in groundwater,
within an underground coal mine, or within the cumulative impact area of
groundwater for which the hydrologic balance has been disturbed from a
permitted coal mine area under the Surface Coal Mining Land Conservation and
Reclamation Act [225 ILCS 720] and 62 Ill. Adm. Code 1700 through 1850, is
subject to this subsection (b).
2) Before completion of reclamation at a coal mine, the standards
specified in Sections 620.410(a) and (e), 620.420(a) and (e), 620.430, and
620.440 do not apply to inorganic constituents and pH.
3) After completion of reclamation at a coal mine, the standards
specified in Sections 620.410(a) and (e), 620.420(a), 620.430, and 620.440 apply
to inorganic constituents and pH, except:
A) The concentration of total dissolved solids (TDS) must not
exceed:
i) The post-reclamation concentration of TDS or 3000 mg/L,
whichever is less, for groundwater within the permitted area; or
ii) The post-reclamation concentration of TDS or 5000 mg/L,
whichever is less, for groundwater in underground coal mines and in permitted
areas reclaimed after surface coal mining if the Illinois Office of Mines and
Minerals, Department of Natural Resources and the Agency have determined that
no significant resource groundwater existed before mining (62 Ill. Adm. Code
1780.21(f) and (g)).
B) The concentration of chloride, iron, manganese, and sulfate, must
not exceed the post-reclamation concentration within the permitted area.
C) pH must not exceed the post-reclamation concentration within
the permitted area in Class I: Potable Resource Groundwater described in
Section 620.210(a)(4).
D) The concentration
of 1,3-dinitrobenzene, 2,4-dinitrotoluene, 2,6-dinitrotoluene, HMX (octahydro-1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetrazocine),
nitrobenzene, RDX (hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine),
1,3,5-trinitrobenzene, and TNT (2,4,6-trinitrotoluene ) must not exceed the
post-reclamation concentration within the permitted area.
4) A refuse disposal area (not contained within the area from
which overburden has been removed) is subject to the inorganic chemical
constituent and pH requirements of:
A) 35 Ill. Adm. Code 302.Subparts B and C, except due to natural
causes, for an area that began operating after February 1, 1983, and before November
25, 1991, if the groundwater is a present or potential source of water for
public or food processing;
B) Section 620.440(c) for an area that began operating before
February 1, 1983, and has remained in continuous operation since that date; or
C) Subpart D for an area that begins operating on or after
November 25, 1991.
5) For a refuse disposal area (not contained within the area from
which overburden has been removed) that began operating before February 1,
1983, and is modified after that date to include additional area, this subsection
(b) applies to the area that complies with subsection (b)(4)(C) and the following
applies to the additional area:
A) 35 Ill. Adm. Code 302.Subparts B and C, except due to natural
causes, for an additional refuse disposal area that began operating after
February 1, 1983, and before November 25, 1991, if the groundwater is a present
or potential source of water for public or food processing; and
B) Subpart D for an additional area that began operating on or
after November 25, 1991.
6) A coal preparation plant (not in an area from which overburden
has been removed) that contains slurry material, sludge, or other precipitated
process material is subject to the inorganic chemical constituent and pH
requirements of:
A) 35 Ill. Adm. Code 302.Subparts B and C, except due to natural
causes, for a plant that began operating after February 1, 1983, and before November
25, 1991, if the groundwater is a present or potential source of water for
public or food processing;
B) Section 620.440(c) for a plant that began operating before
February 1, 1983, and has remained in continuous operation since that date; or
C) Subpart D for a plant that begins operating on or after November
25, 1991.
7) For a coal preparation plant (not in an area from which overburden
has been removed) that contains slurry material, sludge, or other precipitated
process material, began operating before February 1, 1983, and is modified
after that date to include additional area, this subsection (b) applies to the
area that complies with subsection (b)(6)(C) and the following applies to the
additional area:
A) 35 Ill. Adm. Code 302.Subparts B and C, except due to natural
causes, for an additional area that began operating after February 1, 1983, and
before November 25, 1991, if the groundwater is a present or potential source
of water for public or food processing; and
B) Subpart D for an additional area began operating on or after November
25, 1991.
c) Groundwater Quality Standards for Specified Groundwater
Subject to a No Further Remediation Letter under the Site Remediation Program
(35 Ill. Adm. Code 740). While a No Further Remediation Letter is in effect
for a region formerly encompassed by a GMZ established under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 740.530,
the applicable groundwater quality standards for the specified "contaminants
of concern", as defined in 35 Ill. Adm. Code 740.120, within that area are
the groundwater objectives achieved as documented in the approved Remedial
Action Completion Report.
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill. Reg.
4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.505 Compliance
Determination
a) Except as this Part provides otherwise, compliance with the standards
of this Part at a site is to be determined as follows:
1) For a structure (e.g., buildings), at the closest practicable
distance beyond the outermost edge of the structure.
2) For groundwater that underlies a potential primary or
secondary source, the outermost edge as specified in Section 620.240(e)(1).
3) For groundwater that underlies a coal mine refuse disposal
area, a coal combustion waste disposal area, or an impoundment that contains
sludge, slurry, or precipitated process material at a coal preparation plant,
the outermost edge as specified in Section 620.240(f)(1) or the location of
monitoring wells in existence as of November 25, 1991, on a permitted site.
4) For a groundwater management zone, as specified in a
corrective action process.
5) For groundwater, any point where monitoring is conducted using
a water well or a monitoring well that meets one of the following conditions:
A) For a
potable water supply well if:
i) Geologic
logs exist for this well;
ii) Geologic
logs in the immediate 1,000-foot area of this well are representative of the
hydrogeologic materials encountered by this well as determined by a licensed
professional geologist or a licensed professional engineer; or
iii) A WHPA
has been delineated in compliance with the "Guidance Document for
Groundwater Protection Needs Assessments" and "The Illinois Wellhead
Protection Program", incorporated by reference in Section 620.125.
B) For a potable water supply well other than a community water
supply well, a construction report has been filed with the Department of Public
Health for the potable well, or the well has been located and constructed (or
reconstructed) to meet the Illinois Water Well Construction Code [415 ILCS 30]
and 77 Ill. Adm. Code 920.
C) For a potable water supply well that was constructed before
August 20, 1965, the well meets the following criteria:
i) Construction must be done in a manner that will enable the
collection of groundwater samples that represent in situ groundwater
conditions;
ii) Casings and screens must be made from durable material
resistant to expected chemical or physical degradation that do not interfere
with the quality of groundwater samples being collected; and
iii) The annular space opposite the screened section of the well
(i.e., the space between the bore hole and well screen) must be filled with
gravel or sand if necessary to collect groundwater samples. The annular space
above and below the well screen must be sealed to prevent migration of water
from adjacent formations and the surface to the sampled depth.
D) For a community water supply well, the well has been permitted
by the Agency or constructed in compliance with 35 Ill. Adm. Code 602.115.
E) For a water well other than a potable water supply well (e.g.,
a livestock watering well or an irrigation well), a construction report has
been filed with the Department of Public Health or the Office of Mines and
Minerals in the Department of Natural Resources for the well, or the well has
been located and constructed (or reconstructed) to meet the Illinois Water Well
Construction Code [415 ILCS 30] and 35 Ill. Adm. Code 920.
F) For a monitoring well, the well meets the following
requirements:
i) Construction must be done in a manner that will enable the
collection of groundwater samples;
ii) Casings and screens must be made from durable material
resistant to expected chemical or physical degradation that do not interfere
with the quality of groundwater samples being collected; and
iii) The annular space opposite the screened section of the well
(i.e., the space between the bore hole and well screen) must be filled with
gravel or sand if necessary to collect groundwater samples. The annular space
above and below the well screen must be sealed to prevent migration of water
from adjacent formations and the surface to the sampled depth.
6) Monitoring must not be conducted for compliance determinations
under subsection (a):
A) Using a water well that is:
i) Less than 15 feet in total depth from the land surface,
ii) bored or dug,
iii) constructed of permeable materials (e.g., cement, tile, stone,
or brick), and
iv) 36 inches or more in diameter.
B) Using a water well with water quality problems due to damaged well-construction
materials or poorly designed well construction;
C) Using a water well in a basement or pit; or
D) Using water-well water from a holding tank.
b) For a spring, compliance with this Subpart must be determined
at the point of emergence.
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill.
Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.510 Monitoring
and Analytical Requirements
a) Representative Samples
A
representative sample must be taken from locations as specified in Section
620.505.
b) Sampling and Analytical Procedures
1) Samples must be collected in compliance with the procedures specified
in the documents pertaining to groundwater monitoring and analysis incorporated
by reference in Section 620.125 or other procedures adopted by the appropriate
regulatory agency.
2) Groundwater elevation in a groundwater monitoring well must be
determined and recorded when necessary to determine the gradient.
3) Except as specified in other regulations, statistical methods
used to determine naturally occurring groundwater quality background
concentrations of contaminants must be conducted in compliance with "Statistical
Analysis of Groundwater Monitoring Data at RCRA Facilities, (March 2009 Unified
Guidance)", incorporated by reference in Section 620.125, for use with
prediction limits and all other statistical tests, including confidence limits
and control charts.
4) The analytical methodology used for analyzing constituents specified
in Subparts C and D must comply with the following:
A) The methodology must have an LLOQ or LCMRL at or below the
preventive response level of Subpart C or the groundwater standard of Subpart
D, whichever applies; and
B) "Methods for Chemical Analysis of Water and Wastes", "Methods
for the Determination of Inorganic Substances in Environmental Samples", "Methods
for the Determination of Metals in Environmental Samples", "Methods
for the Determination of Organic Compounds in Drinking Water",
"Methods for the Determination of Organic Compounds in Drinking Water,
Supplement I", "Methods for the Determination of Organic Compounds in
Drinking Water, Supplement II", "Methods for the Determination of
Organic Compounds in Drinking Water, Supplement III", "Methods for
the Determination of Organic and Inorganic Compounds in Drinking Water",
"Prescribed Procedures for Measurement of Radioactivity in Drinking
Water", "Procedures for Radiochemical Analysis of Nuclear Reactor
Aqueous Solutions", "Radiochemical Analytical Procedures for Analysis
of Environmental Samples", "Radiochemistry Procedures Manual",
"Practical Guide for Ground Water Sampling", "Test Methods for
Evaluating Solid Wastes, Physical/Chemical Methods" (SW-846), 40 CFR 136, appendix
B, 40 CFR 141.80, 40 CFR 141.61, and 40 CFR 141.62, "Techniques of Water
Resources Investigations of the United States Geological Survey, Guidelines for
Collection and Field Analysis of Ground Water Samples for Selected Unstable
Constituents", "Practical Guide for Ground-Water Sampling",
"Techniques of Water Resources Investigations of the United States
Geological Survey, Guidelines for Collection and Field Analysis of Ground-Water
Samples for Selected Unstable Constituents", or other procedures incorporated
by reference in Section 620.125.
C) When
sampling for Hexafluoropropylene oxide dimer acid (HFPO-DA),
Perfluorobutanesulfonic acid (PFBS), Perfluorohexanesulfonic acid (PFHxS),
Perfluorononanoic acid (PFNA), Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), or Perfluorooctanesulfonic
acid (PFOS), the incorporations by reference in Section 620.125 that apply for
sample collection, preservation, storage, and analysis are:
"Standard Test Method for
Determination of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Water, Sludge,
Influent, Effluent, and Wastewater by Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass
Spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) ASTM D7979-20;
U.S. EPA, Office of Ground Water
and Drinking Water, Standards and Risk Management Division. "Method 533:
Determination of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Drinking Water by
Isotope Dilution Anion Exchange Solid Phase Extraction and Liquid
Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry," November 2019. https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2019-12/documents/method-533-815b19020.pdf;
and
U.S. EPA, Office of Research and
Development, Center for Environmental Solutions & Emergency Response. Shoemaker,
J. and Dan Tettenhorst, Method 537.1: Determination of selected Per- and
Polyfluorinated Alkyl Substances in Drinking Water by Solid Phase Extraction
and Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS). U.S.
Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, Center for
Environmental Assessment, Washington, DC. Version 2.0, March 2020.
c) Reporting Requirements
Groundwater
monitoring analytical results must include information, procedures, and
techniques for:
1) Sample collection (including name of sample collector, time
and date of the sample, method of collection, and identification of the
monitoring location);
2) Sample preservation and shipment (including field quality
control);
3) Analytical procedures (including the MDL, LLOQ, or LCMRL); and
4) Chain of custody control.
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill.
Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.601 Purpose of a
Health Advisory
This Subpart establishes
procedures for issuing a Health Advisory that specifies guidance levels that,
in the absence of standards in Section 620.410, must be considered by the
Agency in:
a) Establishing groundwater cleanup or action levels when there
is a release or substantial threat of a release of:
1) A hazardous substance or pesticide; or
2) Any other contaminant that represents a significant hazard to
public health or the environment.
b) Determining whether a community water supply is taking its raw
water from a site or source in compliance with the siting and source water
requirements of 35 Ill. Adm. Code 604.200.
c) Developing Board rulemaking proposals for new or revised
numerical standards.
d) Evaluating mixtures of chemical substances.
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill. Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.605 Issuance of
a Health Advisory
a) The Agency must issue a Health Advisory for a chemical
substance if the following conditions are met:
1) A community water supply well is sampled and the chemical
substance is detected and confirmed by resampling;
2) There is no standard in Section 620.410 for the chemical
substance; and
3) The chemical substance is toxic or harmful to human health
according to the procedures specified in Appendix A, B, or C.
b) The Health Advisory must contain a general description of the
characteristics of the chemical substance, the potential adverse health
effects, and a guidance level to be determined as follows:
1) If disease or functional impairment is caused due to a
physiological mechanism for which there is a threshold dose below which no
damage occurs, the guidance level for the chemical substance is the Maximum
Contaminant Level Goal (MCLG) adopted by USEPA for the substance, 40 CFR 136, appendix
B, 40 CFR 141.80, 40 CFR 141.61, and 40 CFR 141.62, incorporated by reference in
Section 620.125.
2) If there is no MCLG for the chemical substance, the guidance
level is either the Human Threshold Toxicant Advisory Concentration (HTTAC) or
Human Nonthreshold Toxicant Advisory Concentration (HNTAC) for the substance as
determined in compliance with Appendix A, whichever is less, unless the lower concentration
is less than the substance's lowest appropriate LLOQ specified in "Test
Methods for Evaluating Solid Wastes, Physical/Chemical Methods", EPA
Publication No. SW-846 (SW-846), incorporated by reference in Section 620.125,
or the substance's lowest appropriate LCMRL specified in the drinking water
methods incorporated by reference in Section 620.125.
3) If the lower concentration between the HTTAC and HNTAC of the
chemical substance under subsection (b)(2) is less than its lowest appropriate LLOQ
or LCMRL, the guidance level is the lowest appropriate LLOQ or LCMRL.
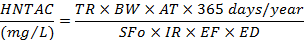
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill.
Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.610 Publishing
Health Advisories
a) The Agency must publish the full text of each Health Advisory
upon issuance and make the document available to the public.
b) The Agency must publish and make available to the public, at
intervals of not more than 6 months, a comprehensive and up-to-date summary
list of all Health Advisories.
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill. Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.615 Additional
Health Advice for Mixtures of Similar-Acting Substances
a) The Agency must determine the need for additional health
advice appropriate to site-specific conditions when mixtures of chemical
substances are detected and two or more of the chemical substances are
similar-acting in their toxic or harmful physiological effect on the same
specific organ or organ system.
b) If mixtures of similar-acting chemical substances are present,
the procedure for evaluating the mixture of the substances is specified in
Appendices A, B, and C.
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill. Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.APPENDIX A Procedures
for Determining Human Toxicant Advisory Concentrations for Class I: Potable
Resource Groundwater
a) Calculating the Human Toxicant Advisory Concentration for
Noncancer Effects
If USEPA has
not adopted a Maximum Contaminant Level Goal (MCLG) for a substance, the Human
Threshold Toxicant Advisory Concentration for the substance is calculated as
follows:

Where:
|
HTTAC
|
=
|
Human Threshold Toxicant
Advisory Concentration in milligrams per liter (mg/L);
|
|
RSC
|
=
|
Relative contribution of the
amount of the exposure to a chemical via drinking water when compared to the
total exposure to that chemical from all sources. Valid chemical-specific
data must be used if available. If valid chemical-specific data are not available,
a value of 20% (= 0.20) must be used;
|
|
ADE
|
=
|
Acceptable Daily Exposure of
substance in milligrams per day (mg/d) as determined under subsection (b);
and
|
|
W
|
=
|
Per capita daily water
consumption for a child (0-6 years of age), equal to 0.78 liters per day
(L/d).
|
b) Procedures for Determining Acceptable Daily Exposures for
Class I: Potable Resource Groundwater
1) The Acceptable Daily Exposure (ADE) represents the maximum
amount of a threshold toxicant in milligrams per day (mg/d) that, if ingested
daily by a child from 0-6 years of age, results in no adverse effects.
Subsections (b)(2) through (b)(6) list, in prescribed order, methods for
determining the ADE in Class I: Potable Resource Groundwater.
2) If the noncancer toxicity value of a substance has been
derived and presented in milligrams per kilogram per day (mg/kg/day), the ADE of
the substance equals the product of multiplying the toxicity value by 15
kilograms (kg), which is the assumed average weight of a child 0 to 6 years of
age.
3) If the oral reference dose of a substance is not available,
the ADE of the substance equals the value of the most sensitive Point of
Departure (POD) as determined by Benchmark Dose Modeling or the NOAEL/LOAEL
approach consistent with current USEPA RfD guidance, followed by the derivation
of a Human Equivalent Dose (HED) using physiologically based pharmacokinetic
(PBPK) modeling or Dose Adjustment Factor (DAF), then divided by the total
Uncertainty Factor (UF) and modifying factor (MF), if applicable. The value is
then multiplied by 15 kg (the assumed average weight of a child 0-6 years of
age). The equation is as follows:

4) Uncertainty
Factors must be applied to the Point of Departure (POD) in increments of 1, 3,
or 10, not to exceed a total UF of 10,000, and must be used consistent with
USEPA guidance. A composite UF of 3 and 10 must be expressed as 30. A composite
UF of 3 and 3 must be expressed as 10. UFs may be used to account for the
following:
A) Interspecies Variability
B) Intraspecies Variability
C) Lowest
Observable Adverse Effects Level (LOAEL) to No Observed Adverse Effects Level
(NOAEL) Uncertainty
D) Database Deficiencies
E) Subchronic to Chronic
Duration
c) Procedures for Establishing Validity of Data from Animal
Studies
1) High Validity Studies
A) High validity studies use a route of exposure by ingestion or
gavage, and are based upon:
i) Data from animal carcinogenicity studies with a minimum of 2
dose levels and a control group, 2 species, both sexes, with 50 animals per
dose per sex, and at least 50 percent survival at 15 months in mice and 18
months in rats and at least 25 percent survival at 18 months in mice and 24
months in rats;
ii) Data from animal chronic studies with a minimum of 3 dose
levels and a control group, 2 species, both sexes, with 40 animals per dose per
sex, and at least 50 percent survival at 15 months in mice and 18 months in
rats and at least 25 percent survival at 18 months in mice and 24 months in
rats, and a well-defined NOAEL; or
iii) Data from animal subchronic studies with a minimum of 3 dose
levels and control, 2 species, both sexes, 4 animals per dose per sex for
non-rodent species or 10 animals per dose per sex for rodent species, a
duration of at least 5% of the test species' lifespan, and a well-defined NOAEL.
B) Supporting studies that reinforce the conclusions of a study of
Medium Validity may be considered to raise the study to High Validity.
2) Medium Validity Studies
Medium
validity studies are based upon:
A) Data from animal carcinogenicity, chronic, or subchronic
studies in which minor deviations from the study design elements required for a
High Validity Study are found, but that otherwise satisfy the standards for a
High Validity Study;
B) Data from animal carcinogenicity and chronic studies in which
at least 25 percent survival is reported at 15 months in mice and 18 months in
rats (a lesser survival is permitted at the conclusion of a longer duration
study but the number of surviving animals must not fall below 20 percent per
dose per sex at 18 months for mice and 24 months for rats), but that otherwise
satisfy the standards for a High Validity Study;
C) Data from animal subchronic or chronic studies in which a
Lowest Observable Adverse Effect Level (LOAEL) is determined, but that
otherwise satisfy the standards for a High Validity Study; or
D) Data from animal subchronic or chronic studies that have an
inappropriate route of exposure (e.g., intraperitoneal injection or inhalation),
but that otherwise satisfy the standards for a High Validity Study, with
correction factors for conversion to the oral route.
3) Low Validity Studies
Low validity
studies are studies not meeting the standards specified in subsection (c)(1) or
(c)(2).
d) Calculating
a Human Nonthreshold Toxicant Advisory Concentration (HNTAC) for Cancer Risk
The Human Nonthreshold Toxicant
Advisory Concentration (HNTAC) is calculated as follows:
1) If
USEPA has designated a chemical as a "mutagen", the HNTAC of the
chemical is calculated as follows:

Where:
|
HNTAC
|
=
|
Human Nonthreshold Toxicant
Advisory Concentration, equal to milligrams per liter (mg/L)
|
|
TR
|
=
|
Target Cancer Risk, equal to one-in-one
million cancer risk (1E-06)
|
|
AT
|
=
|
Averaging Time, equal to 70
years
|
|
SFo
|
=
|
Oral Slope Factor
(chemical-specific), equal to (mg/kg-day)-1
|
|
IFWMadj
|
=
|
Age-Adjusted Mutagenic
Drinking Water Ingestion Rate, equal to 1,019.0 liters per kilogram (L/kg)
|
2) If
USEPA has not designated a chemical as a "mutagen", the HNTAC of the
chemical is calculated as follows:

Where:
|
HNTAC
|
=
|
Human Nonthreshold Toxicant
Advisory Concentration, equal to milligrams per liter (mg/L)
|
|
TR
|
=
|
Target Cancer Risk, equal to
one-in-one million cancer risk (1E-06)
|
|
AT
|
=
|
Averaging Time, equal to 70
years
|
|
SFo
|
=
|
Oral Slope Factor
(chemical-specific), equal to (mg/kg-day)-1
|
|
IFWMadj
|
=
|
Age-Adjusted Mutagenic
Drinking Water Ingestion Rate, equal to 327.95 liters per kilogram (L/kg)
|
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill.
Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.APPENDIX B Procedures
for Determining Hazard Indices for Class I: Potable Resource Groundwater for
Mixtures of Similar-Acting Substances
a) This appendix describes procedures for evaluating mixtures of
similar-acting substances that may be present in Class I: Potable Resource
Groundwaters. Except as provided otherwise in subsection (c), subsections (d)
through (h) describe the procedure for determining the Hazard Index for
mixtures of similar-acting substances.
b) For this appendix, a "mixture" means two or more
substances present in Class I: Potable Resource Groundwater that may or may
not be related either chemically or commercially but are not complex mixtures
of related isomers and congeners produced as commercial products (e.g., PCBs or
technical grade chlordane).
c) The substances specified in Section 620.Appendix E are similar-acting
substances.
d) When two or more substances occur together in a mixture, the
additivity of the toxicities of some or all of the substances must be
considered when determining health-based standards for Class I: Potable
Resource Groundwater. This is done by using a dose addition model with the
development of a Hazard Index for the mixture of substances with similar-acting
toxicities. This method does not address synergism or antagonism. Guidelines
for determining when the dose addition of similar-acting substances is
appropriate are presented in Appendix C. The Hazard Index is calculated as
follows:
HI = [A]/ALA + [B]/ALB +. . . [I]/ALI
Where:
|
HI
|
=
|
Hazard Index, unitless.
|
|
[A], [B], [I]
|
=
|
Concentration of each
similar-acting substance in groundwater in milligrams per liter (mg/L).
|
|
ALA, ALB, ALI
|
=
|
The acceptable level of each
similar-acting substance in the mixture in milligrams per liter (mg/L).
|
e) For a substance with a threshold mechanism of toxicity, the substance's
acceptable level in subsection (d) is:
1) The substance's standard specified in Section 620.410; or
2) The substance's Human Threshold Toxicant Advisory
Concentration (HTTAC) as determined in Appendix A if the substance has no
standard specified in Section 620.410.
f) For a carcinogenic substance, the substance's acceptable level
in subsection (d) is:
1) The substance's standard specified in Section 620.410; or
2) If a substance has no standard specified in Section 620.410, the
substance's one-in-one-million cancer risk concentration, unless that
concentration is less than the substance's lowest appropriate LLOQ specified in
"Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Wastes, Physical/Chemical Methods",
EPA Publication No. SW-846, incorporated by reference in Section 620.125, or
the substance's lowest appropriate LCMRL specified in the drinking water
methods incorporated by reference in Section 620.125. If the one-in-one-million
cancer risk concentration is less than the lowest appropriate LLOQ or LCMRL, the
acceptable level is the lowest appropriate LLOQ or LCMRL.
g) Because the assumption of dose addition is most properly
applied to substances that induce the same effect by similar modes of action, a
separate Hazard Index must be generated for each toxicity endpoint of concern.
h) In addition to meeting the individual substance objectives, a
Hazard Index must be less than or equal to 1 for a mixture of similar-acting
substances.
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill.
Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.APPENDIX C Guidelines
for Determining When Dose Addition of Similar-Acting Substances in Class I:
Potable Resource Groundwaters is Appropriate
a) Substances must be considered similar-acting if:
1) The substances have the same target in an organism (e.g., the
same organ, organ system, receptor, or enzyme); or
2) The substances have the same mode of toxic action. These
actions may include, for example, central nervous system depression, liver
toxicity, and cholinesterase inhibition.
b) Substances that have fundamentally different mechanisms of
toxicity (threshold toxicants vs. carcinogens) must not be considered
similar-acting. However, carcinogens that also cause a threshold toxic effect must
be considered in a mixture with other similar-acting substances having the same
threshold toxic effect. In that case, an acceptable level of the carcinogen
must be derived for its threshold effect, using the procedures specified in
Appendix A.
c) Substances that are components of a complex mixture of related
compounds produced as commercial products (e.g., PCBs or technical grade
chlordane) are not mixtures, as defined in Appendix B. These complex mixtures
are equivalent to a single substance. In that case, the Human Threshold
Toxicant Advisory Concentration (HTTAC) must be derived for threshold effects
of the complex mixture, using the procedures specified in Appendix A, if valid
toxicological or epidemiological data are available for the complex mixture.
If the complex mixture is a carcinogen, the Human Nonthreshold Toxicant
Advisory Concentration (HNTAC) is the one-in-one-million cancer risk
concentration, calculated from methods located at Appendix A. The guidance
level is either the HTTAC or HNTAC, whichever is less unless the lower concentration
is less than the substance's lowest appropriate LLOQ specified in "Test
Methods for Evaluating Solid Wastes, Physical/Chemical Methods", EPA
Publication No. SW-846, incorporated by reference in Section 620.125, or the substance's
lowest appropriate LCMRL specified in the drinking water methods incorporated
by reference in Section 620.125. If the lower concentration between the HTTAC
and HNTAC of the substance is less than its lowest appropriate LLOQ or LCMRL,
the guidance level is the lowest appropriate LLOQ or LCMRL.
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill.
Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.APPENDIX D Information
Required for Groundwater Management Zone Application under 35 Ill. Adm. Code
620.250(b) and Corrective Action Completion Certification under 35 Ill. Adm.
Code 620.250(d)
Within any class of groundwater,
a groundwater management zone (GMZ) may be established as a three-dimensional
region containing groundwater being managed to mitigate impairment caused by a release
of one or more contaminants that is subject to a corrective action process
approved by the Illinois Environmental Protection Agency (Agency). See 35 Ill.
Adm. Code 620.250(a). A GMZ cannot be established before the site owner or
operator submits a GMZ application to the Agency under 35 Ill. Adm. Code
620.250(b). A GMZ is not established until the Agency issues a written
approval of the GMZ, including its corrective action process, under 35 Ill.
Adm. Code 620.250(c)(2).
When an owner or operator
completes the Agency-approved corrective action, the owner or operator must
submit to the Agency appropriate documentation under 35 Ill. Adm. Code
620.250(d), including the information required for a corrective action
completion certification. A GMZ is terminated when the Agency issues a written
determination to that effect under 35 Ill. Adm. Code 620.250(c)(2)(i),
(c)(2)(ii), (d)(1), or (f).
|
Note 1.
|
Parts I, II,
and III of this Appendix D specify the information required for the GMZ
application that the owner or operator submits to the Agency. See 35 Ill.
Adm. Code 620.250(b). Part IV of this Appendix D specifies the information
required for the corrective action completion certification that the owner or
operator submits to the Agency. See 35 Ill. Adm. Code 620.250(d). The owner
or operator is neither required to use the form specified in Part I, II, III,
or IV of this Appendix D nor precluded from including information in addition
to that required by this Appendix D. See 35 Ill. Adm. Code 620.250(b)(2),
(b)(3), (d).
|
|
Note 2.
|
The issuance
of a permit by the Agency's Division of Air Pollution Control or Water
Pollution Control for a treatment system does not imply that the Agency has
approved any corrective action process.
|
|
Note 3.
|
Parts I, II,
and III of this Appendix D are not for use in establishing a GMZ under the
Site Remediation Program (35 Ill. Adm. Code 740). See 35 Ill. Adm. Code
620.250(h).
|
|
Note 4.
|
If the GMZ
would extend off-site, the GMZ application must include each off-site property
owner's written permission to the establishment of the GMZ on its property.
If effectively implementing the off-site portion of the GMZ requires
accessing an off-site property, the GMZ application must also include the
off-site property owner's written permission for that access. If the
applicable written permission or permissions from an off-site property owner
are not obtained—whether permission to establish the GMZ off-site, access the
off-site property, or both—the GMZ will not include that off-site property.
See 35 Ill. Adm. Code 620.250(b)(1).
|
|
Note 5.
|
If a response to any item in this Appendix D requires
additional explanation or clarification, provide it in an attachment to the
submittal.
|
|
Part I:
|
Facility Information
|
|
|
Facility Name
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Facility Address
|
|
|
|
|
|
County
|
|
|
|
|
|
Standard
Industrial Code (SIC)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. Provide a general description of the type of industry and the
facility's location and size, as well as the products manufactured and raw
materials used at the facility.
2. What specific units (operating or closed) are present at the
facility that are or were used to manage waste, hazardous waste, hazardous
substances, or petroleum? Include units regardless of whether they are
considered sources of groundwater contamination.
|
|
YES
|
|
NO
|
|
Landfill
|
|
|
|
|
Surface Impoundment
|
|
|
|
|
Land Treatment
|
|
|
|
|
Spray Irrigation
|
|
|
|
|
Waste Pile
|
|
|
|
|
Incinerator
|
|
|
|
|
Storage Tank (above ground)
|
|
|
|
|
Storage Tank (underground)
|
|
|
|
|
Container Storage Area
|
|
|
|
|
Injection Well
|
|
|
|
|
Water Treatment Units
|
|
|
|
|
Septic Tanks
|
|
|
|
|
French Drains
|
|
|
|
|
Transfer Station
|
|
|
|
|
Other Units (describe)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. Provide an extract from a USGS topographic or county map
showing the location of the site. Provide a more detailed scaled map of the
facility identifying each unit checked "yes" in item 2 and each known
or suspected release source. Map scale must be specified and the Township,
Range, and Section of the facility must be provided. Also provide engineering
drawings showing the facility and units at the facility.
4. Has the facility ever conducted operations that involved the generation,
manufacture, processing, transportation, treatment, storage, or handling of
"hazardous substances" as defined by the Illinois Environmental
Protection Act? Yes ___No ___ If the answer to this question is
"yes", generally describe these operations.
5. Has the facility ever generated, stored, or treated "hazardous
waste" as defined by the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA)?
Yes ___ No ___If the answer to this question is "yes",
generally describe these operations.
6. Has the facility ever conducted operations that involved the
processing, storage, or handling of petroleum? Yes ___No ____If
the answer to this question is "yes", generally describe these operations.
7. Has the facility ever held any of the following permits?
a. Permits for any waste storage, waste treatment, or waste
disposal operation. Yes ___ No ___ If the answer to this
question is "yes", identify the IEPA permit number or numbers.
b. Interim Status under RCRA (filing of a RCRA Part A
application). Yes ___ No ___ If the answer to this question is
"yes", attach a copy of the last approved RCRA Part A application.
c. RCRA Part B permits. Yes ___ No ___ If the
answer to this question is "yes", identify the permit log number or
numbers.
8. Has the facility ever conducted the closure of a RCRA
hazardous waste management unit? Yes ___ No ___
9. Have any of the following State or federal government actions
taken place for a release at the facility?
a. Written notification regarding known, suspected, or alleged
contamination at the property (e.g., a Notice under Section 4(q) or Section
31(a) or (b) of the Illinois Environmental Protection Act)? Yes ___ No ___
If the answer to this question is "yes", identify notice's caption
and date of issuance.
b. Consent Decree or Order under RCRA, the Comprehensive
Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA), Section 22.2 of
the Illinois Environmental Protection Act (State Superfund), or Section 21(f) of
the Illinois Environmental Protection Act (State RCRA). Yes ___ No ___
c. If either item 9(a) or 9(b) is answered "yes", is
the notice, order, or decree still in effect? Yes ___ No ___
10. Provide
a statement of the classification or classifications of groundwater at the
facility.
Class I ____ Class II
____ Class III ____ Class IV ____
If more than one Class applies,
explain.
11. What classification will the groundwater within the proposed
groundwater management zone be subject to at the completion of the remediation?
Class I ____ Class
II ____ Class III ____ Class IV ____
If more than one Class applies, explain.
12. Describe the circumstances under which the release to
groundwater was identified.
Based on my inquiry of those
persons directly responsible for gathering the information, I certify that the
information submitted is, to the best of my knowledge and belief, true and
accurate.
|
|
|
|
|
Facility
Name
|
|
Signature of Owner/Operator
|
|
|
|
Location of
Facility
|
|
Name of Owner/Operator
|
|
|
|
EPA
Identification Number
|
|
Date
|
Part II: Release Information
1. Identify the chemical constituents released to the
groundwater. Attach additional documents as necessary.
|
Chemical
Description
|
|
Chemical
Abstract No.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Describe how the site will be investigated to determine the
source or sources of the release.
3. Describe how groundwater will be monitored to determine the rate
and extent of the release, and whether the release has migrated off-site.
4. Has the release been contained on-site?
5. Describe the groundwater monitoring network and groundwater and
soil sampling protocols in place at the facility.
6. Provide the schedule for investigating the extent of the release
and for monitoring.
7. Describe the laboratory quality assurance program used for the
investigation.
8. Provide the results of available soil testing and groundwater
monitoring associated with the release, along with a summary of those results.
Include the following information: dates of sampling; types of samples taken
(soil or water); locations and depths of samples; monitoring well construction
details with well logs; sampling and analytical methods; analytical
laboratories used; chemical constituents for which analyses were performed;
analytical detection limits; and concentrations of chemical constituents in parts
per million or "ppm" (levels below detection must be identified as non-detect
or "ND").
9. Provide scaled drawings identifying the horizontal and vertical
boundaries of the proposed groundwater management zone.
Based on my inquiry of those
persons directly responsible for gathering the information, I certify that the
information submitted is, to the best of knowledge and belief, true and
accurate and confirm that the actions identified in this submittal will be performed
in compliance with the schedule in this submittal.
|
|
|
|
|
Facility
Name
|
|
Signature of Owner/Operator
|
|
|
|
Location of
Facility
|
|
Name of Owner/Operator
|
|
|
|
EPA
Identification Number
|
|
Date
|
Part III: Remedy Selection
Information
1. Describe the selected remedy and why it was chosen. Include a
description of the fate and transport of contaminants with the selected remedy
over time.
2. Describe other remedies that were considered and why they were
rejected.
3. Will waste, contaminated soil, or contaminated groundwater be
removed from the site during this remediation? Yes ___ No ___ If
the answer to this question is "yes", where will the contaminated
material be taken?
4. Describe how the selected remedy will accomplish the maximum practicable
restoration of beneficial use of groundwater.
5. Describe how the selected remedy will minimize any threat to
public health or the environment.
6. Describe how the selected remedy will result in compliance
with the standards for the applicable class or classes of groundwater. Include
the results of groundwater contaminant transport modeling or calculations
showing how the selected remedy will achieve compliance with these standards.
7. Provide a schedule for design, construction, and operation of
the remedy, including dates for the start and completion.
8. Describe how the remedy will be operated and maintained.
9. Have any of the following permits been issued for the
remediation?
a. Construction or operating permit from the Agency's Division of
Water Pollution Control. Yes __ No ___ If the answer to this
question is "yes", identify the permit number or numbers.
b. Land treatment permit from the Agency's Division of Water
Pollution Control. Yes ___ No ___ If the answer to this question
is "yes", identify the permit number or numbers.
c. Construction or operating permit from the Agency's Division of
Air Pollution Control. Yes ___ No ___ If the answer to this
question is "yes", identify the permit number or numbers.
10. How will groundwater within the proposed groundwater management
zone be monitored after completion of the remedy to ensure compliance with the standards
for the applicable class or classes of groundwater?
Based on my
inquiry of those persons directly responsible for gathering the information, I
certify that the information submitted is, to the best of my knowledge and belief,
true and accurate and confirm that the actions identified in this submittal will
be performed in compliance with the schedule in this submittal.
|
|
|
|
|
Facility
Name
|
|
Signature of Owner/Operator
|
|
|
|
|
Location of
Facility
|
|
Name of Owner/Operator
|
|
|
|
|
EPA
Identification Number
|
|
Date
|
Part IV: Corrective Action Completion
Certification
This certification must
accompany documentation that includes soil and groundwater monitoring data
demonstrating completion of the corrective action.
|
Facility Name
|
|
|
|
|
|
Facility Address
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
County
|
|
|
|
|
|
Standard Industrial Code (SIC)
|
|
|
|
|
Date
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Based on my inquiry of those
persons directly responsible for gathering the information, I certify that the corrective
action approved by the Illinois Environmental Protection Agency has been completed
and the following concentrations of released chemical constituents remain in
groundwater within the groundwater management zone:
|
Chemical Name
|
|
Chemical
Abstract No.
|
|
Concentration
(mg/L)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Facility
Name
|
|
Signature of Owner/Operator
|
|
|
|
|
Location of
Facility
|
|
Name of Owner/Operator
|
|
|
|
|
EPA
Identification Number
|
|
Date
|
(Source: Amended at 49 Ill.
Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.APPENDIX E
Similar-Acting Substances
620.TABLE A Similar-Acting
Noncarcinogenic Constituents
|
Cholinesterase
Inhibition
|
|
|
116-06-3
|
Aldicarb
|
|
1563-66-2
|
Carbofuran
|
|
|
|
|
Circulatory System
|
|
|
15972-60-8
|
Alachlor
|
|
7440-36-0
|
Antimony
|
|
1912-24-9
|
Atrazine
|
|
71-43-2
|
Benzene
|
|
94-75-7
|
2,4-D
(2,4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid)
|
|
121-14-2
|
2,4-Dinitrotoluene
|
|
206-44-0
|
Fluoranthene
|
|
86-73-7
|
Fluorene
|
|
98-95-3
|
Nitrobenzene
|
|
122-34-9
|
Simazine
|
|
100-42-5
|
Styrene
|
|
79-01-6
|
Trichloroethylene
|
|
99-35-4
|
1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene
|
|
7440-66-6
|
Zinc
|
|
|
|
|
Decreased Body Weight
|
|
|
75-71-8
|
Dichlorodifluoromethane
|
|
84-66-2
|
Diethyl phthalate
|
|
95-48-7
|
2-Methylphenol (o-cresol)
|
|
91-20-3
|
Naphthalane
|
|
7440-02-0
|
Nickel
|
|
108-95-2
|
Phenol
|
|
122-34-9
|
Simazine
|
|
71-55-6
|
1,1,1-Trichloroethane
|
|
1330-20-7
|
Xylenes
|
|
|
|
|
Developmental
|
|
|
7429-90-5
|
Aluminum
|
|
50-32-8
|
Benzo(a)pyrene
|
|
7440-42-8
|
Boron
|
|
78-93-3
|
2-Butanone (methyl ethyl
ketone)
|
|
75-15-0
|
Carbon disulfide
|
|
78-87-5
|
1,2-Dichloropropane
|
|
84-66-2
|
Diethyl phthalate
|
|
88-85-7
|
Dinoseb
|
|
7439-93-2
|
Lithium
|
|
375-73-5
|
PFBS
(perfluorobutanesulfonic acid)
|
|
375-95-1
|
PFNA (perfluorononanoic
acid)
|
|
1763-23-1
|
PFOS
(perfluorooctanesulfonic acid)
|
|
335-67-1
|
PFOA (perfluorooctanoic
acid)
|
|
|
|
|
Endocrine System
|
|
|
106-93-4
|
Ethylene dibromide
(1,2-dibromoethane)
|
|
120-82-1
|
1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene
|
|
|
|
|
Gastrointestinal
System
|
|
|
7440-41-7
|
Beryllium
|
|
7440-50-8
|
Copper
|
|
145-73-3
|
Endothall
|
|
77-47-4
|
Hexachlorocyclopentadiene
|
|
7439-89-6
|
Iron
|
|
1634-04-4
|
MTBE (methyl
tertiary-butyl-ether)
|
|
|
|
|
Immune System
|
|
|
156-60-5
|
trans-1,2-Dichloroethylene
|
|
58-89-9
|
gamma-HCH (gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane, lindane)
|
|
7487-94-7
|
Mercury (mercuric
chloride)
|
|
76-44-8
|
Heptachlor
|
|
355-46-4
|
PFHxS
(perfluorohexanesulfonic acid)
|
|
375-95-1
|
PFNA (perfluorononanoic
acid)
|
|
1763-23-1
|
PFOS
(perfluorooctanesulfonic acid)
|
|
335-67-1
|
PFOA (perfluorooctanoic
acid)
|
|
|
|
|
Kidney
|
|
|
7440-39-3
|
Barium
|
|
7440-43-9
|
Cadmium
|
|
94-75-7
|
2,4-D (2,4-dichlorophenoxy
acetic acid)
|
|
75-99-0
|
Dalapon
|
|
75-34-3
|
1,1-Dichloroethane
|
|
107-06-2
|
1,2-Dichloroethane
|
|
156-59-2
|
cis-1,2-Dichloroethylene
|
|
123-91-1
|
1,4-Dioxane (p-dioxane)
|
|
206-44-0
|
Fluoranthene
|
|
98-82-8
|
Isopropylbenzene (cumene)
|
|
7439-93-2
|
Lithium
|
|
93-65-2
|
MCPP (mecoprop)
|
|
7487-94-7
|
Mercury (mercuric
chloride)
|
|
7439-98-7
|
Molybdenum
|
|
129-00-0
|
Pyrene
|
|
108-88-3
|
Toluene
|
|
7440-62-2
|
Vanadium
|
|
|
|
|
Liver
|
|
|
83-32-9
|
Acenaphthene
|
|
319-84-6
|
alpha-BHC (alpha-benzene hexachloride)
|
|
56-23-5
|
Carbon Tetrachloride
|
|
12789-03-6
|
Chlordane
|
|
108-90-7
|
Chlorobenzene
|
|
67-66-3
|
Chloroform
|
|
94-75-7
|
2,4-D (2,4-dichlorophenoxy
acetic acid)
|
|
106-46-7
|
p-Dichlorobenzene (1,4-dichlorobenzene)
|
|
75-35-4
|
1,1-Dichloroethylene
|
|
75-09-2
|
Dichloromethane
(methylene chloride)
|
|
117-81-7
|
Di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate
|
|
121-14-2
|
2,4-Dinitrotoluene
|
|
123-91-1
|
1,4-Dioxane (p-dioxane)
|
|
72-20-8
|
Endrin
|
|
100-41-4
|
Ethylbenzene
|
|
106-93-4
|
Ethylene dibromide
(1,2-dibromoethane)
|
|
206-44-0
|
Fluoranthene
|
|
13252-13-6
|
HFPO-DA
(hexafluoropropylene oxide dimer acid, GenX)
|
|
2691-41-0
|
HMX (octahydro-1,3,5,7-tetranitro-1,3,5,7-tetrazocine)
|
|
1024-57-3
|
Heptachlor Epoxide
|
|
1634-04-4
|
MTBE (methyl
tertiary-butyl ether)
|
|
87-86-5
|
Pentachlorophenol
|
|
1918-02-1
|
Picloram
|
|
100-42-5
|
Styrene
|
|
118-96-7
|
TNT
(2,4,6-trinitrotoluene)
|
|
93-72-1
|
2,4,5-TP (silvex)
|
|
75-01-4
|
Vinyl Chloride
|
|
|
|
|
Lungs
|
|
|
90-12-0
|
1-Methylnaphthalene
|
|
91-57-6
|
2-Methylnaphthalene
|
|
|
|
|
Mortality
|
|
|
84-74-2
|
Di-n-butyl
phthalate
|
|
1330-20-7
|
Xylenes
|
|
|
|
|
Nervous System
|
|
|
67-64-1
|
Acetone
|
|
121-14-2
|
2,4-Dinitrotoluene
|
|
72-20-8
|
Endrin
|
|
7439-93-2
|
Lithium
|
|
7439-96-5
|
Manganese
|
|
95-48-7
|
2-Methylphenol (o-cresol)
|
|
121-82-4
|
RDX
(hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro- l,3,5-triazine)
|
|
127-18-4
|
Tetrachloroethylene
|
|
|
|
|
Reproductive System
|
|
|
1912-24-9
|
Atrazine
|
|
96-12-8
|
1,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane
|
|
1563-66-2
|
Carbofuran
|
|
75-15-0
|
Carbon disulfide
|
|
143-33-9
|
Cyanide
|
|
1918-00-9
|
Dicamba
|
|
106-93-4
|
Ethylene dibromide
(1,2-dibromoethane)
|
|
7439-93-2
|
Lithium
|
|
72-43-5
|
Methoxychlor
|
|
|
|
|
Skin
|
|
|
7440-38-2
|
Arsenic
|
|
7440-22-4
|
Silver
|
|
7440-28-0
|
Thallium
|
|
|
|
|
Spleen
|
|
|
99-65-0
|
1,3-Dinitrobenzene
|
|
606-20-2
|
2,6-Dinitrotoluene
|
|
99-35-4
|
1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene
|
|
|
|
|
Thyroid
|
|
|
7440-48-4
|
Cobalt
|
|
14797-73-0
|
Perchlorate
|
|
355-46-4
|
PFHxS
(perfluorohexanesulfonic acid)
|
|
375-73-5
|
PFBS
(perfluorobutanesulfonic acid)
|
|
8001-35-2
|
Toxaphene
|
|
|
|
|
Whole Body
|
|
|
120-12-7
|
Anthracene
|
|
7440-36-0
|
Antimony
|
|
65-85-0
|
Benzoic Acid
|
|
95-50-1
|
o-Dichlorobenzene (1,2-dichlorobenzene)
|
|
206-44-0
|
Fluoranthene
|
|
7782-49-2
|
Selenium
|
|
79-00-5
|
1,1,2-Trichloroethane
|
|
75-69-4
|
Trichlorofluoromethane
|
(Source:
Added at 49 Ill. Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
Section 620.APPENDIX E Similar-Acting Substances
620.TABLE B Similar-Acting
Carcinogenic Constituents
|
Circulatory System
|
|
|
71-43-2
|
Benzene
|
|
107-06-2
|
1,2-Dichloroethane
|
|
106-93-4
|
Ethylene dibromide (1,2-dibromoethane)
|
|
|
|
|
Gastrointestinal
System
|
|
|
56-55-3
|
Benzo(a)anthracene
|
|
205-99-2
|
Benzo(b)fluoranthene
|
|
207-08-9
|
Benzo(k)fluoranthene
|
|
50-32-8
|
Benzo(a)pyrene
|
|
218-01-9
|
Chrysene
|
|
53-70-3
|
Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene
|
|
106-93-4
|
Ethylene dibromide (1,2-dibromoethane)
|
|
193-39-5
|
Indeno(1,2,3-c,d)pyrene
|
|
|
|
|
Kidney
|
|
|
67-66-3
|
Chloroform
|
|
96-12-8
|
1,2-Dibromo-3-chloropropane
(dibromochloropropane)
|
|
121-14-2
|
2,4-Dinitrotoluene
|
|
606-20-0
|
2,6-Dinitrotoluene
|
|
100-41-4
|
Ethylbenzene
|
|
79-01-6
|
Trichloroethylene
|
|
|
|
|
Liver
|
|
|
319-84-6
|
alpha-BHC (alpha-benzene
hexachloride)
|
|
56-23-5
|
Carbon tetrachloride
|
|
12789-03-6
|
Chlordane
|
|
106-46-7
|
p-Dichlorobenzene (1,4-dichlorobenzene)
|
|
75-09-2
|
Dichloromethane
(methylene chloride)
|
|
78-87-5
|
1,2-Dichloropropane
|
|
117-81-7
|
Di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate
|
|
121-14-2
|
2,4-Dinitrotoluene
|
|
606-20-0
|
2,6-Dinitrotoluene
|
|
123-91-1
|
1,4-Dioxane (p-dioxane)
|
|
58-89-9
|
gamma-HCH (gamma
-hexachlorocyclohexane, lindane)
|
|
76-44-8
|
Heptachlor
|
|
1024-57-3
|
Heptachlor epoxide
|
|
1336-36-3
|
PCBs (polychlorinated
biphenyls as decachloro-biphenyl)
|
|
335-67-1
|
PFOA (perfluorooctanoic
acid)
|
|
87-86-5
|
Pentachlorophenol
|
|
127-18-4
|
Tetrachloroethylene
|
|
8001-35-2
|
Toxaphene
|
|
79-01-6
|
Trichloroethylene
|
|
75-01-4
|
Vinyl Chloride
|
|
|
|
|
Mammary Gland
|
|
|
121-14-2
|
2,4-Dinitrotoluene
|
|
606-20-0
|
2,6-Dinitrotoluene
|
(Source:
Added at 49 Ill. Reg. 4488, effective March 28, 2025)
![]()
![]()
![]()

